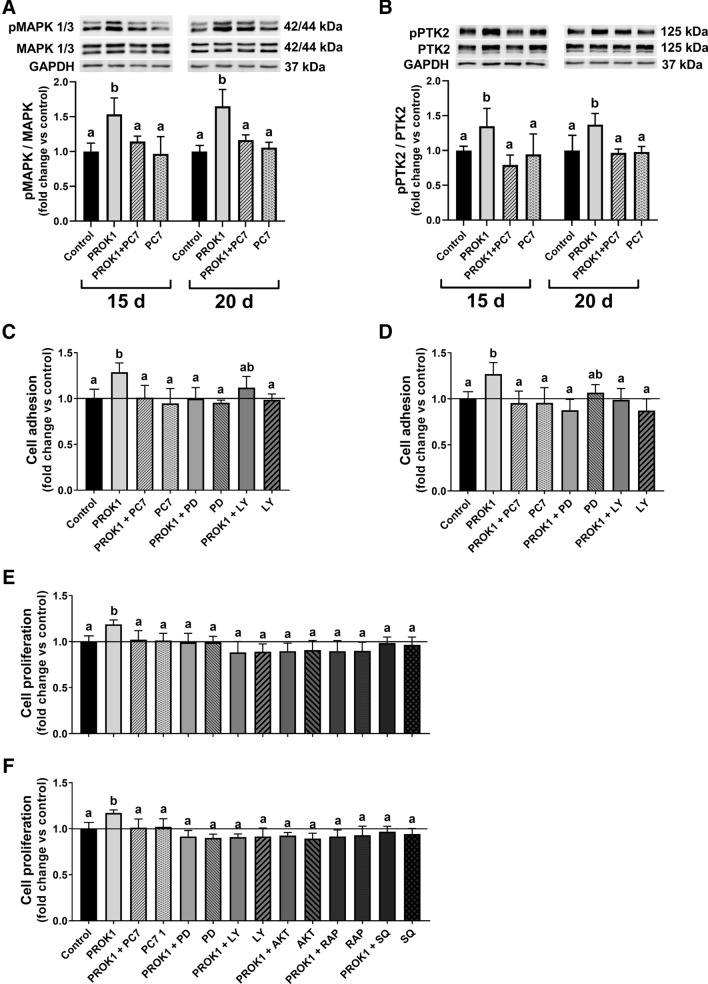
Figure 6.
Prokineticin 1 (PROK1) stimulated trophoblast cell proliferation and adhesion and activates signaling pathways involved in these processes. The effects of PROK1 on processes involved in the porcine trophoblast cell proliferation, adhesion and invasion. PROK1 increases phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK1/3) (A) and protein tyrosine kinase 2 (PTK2) (B) in trophoblast cells after 10 min of treatment in vitro. Representative samples of Western blots for MAPK1/3, pMAPK1/3, PTK2, and pPTK2 are shown in the upper part of (A) and (B). Full-length Western blots are presented in Supplementary Figs. 1 and 2. PROK1 stimulates adhesion and proliferation of trophoblast cells isolated on days 15 (C,E, respectively) and 20 (D and F, respectively) of pregnancy. Trophoblast cells were incubated for 24 h with the control (vehicle; 0.01% ethanol) or PROK1 in the presence/absence of a PROKR1 antagonist (PC7; 1 μM) and inhibitors of MAPK (PD 098059; 25 μM), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K; LY 294002; 25 μM)—for adhesion and proliferation assay; and inhibitors of protein kinase B (AKT; 2.5 μM), mTOR (rapamycin, RAP; 50 nM), and cAMP synthesis (SQ 22536; 25 μM)—only for proliferation assay. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of the fold change versus control. Different letters (a–b) indicate statistically significant differences (P < 0.05). Means marked by the same letter indicate no significant difference.