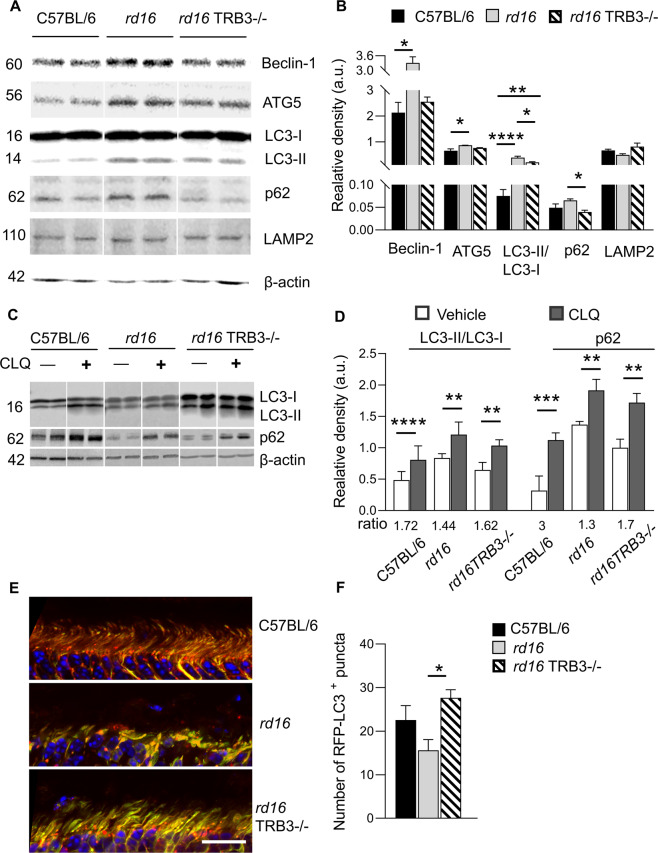
Fig. 4. TRB3 ablation in P15 rd16 retinas resulted in restoration of autophagy-associated protein levels and flux.
A Images of western blot membranes probed with anti-Beclin-1, ATG5, LC3, p62, and LAMP2 antibodies. B Quantitation of Beclin-1, ATG5, LC3 II/I, p62, and LAMP2 in protein retinal extracts from three groups of mice (n = 4–5). C, D Treatment of retinal explants with chloroquine (CLQ), a classic inhibitor of autophagy, was used to determine the capacity of degenerating retinas to promote autophagosome fusion with lysosomes. C Images of western blot analysis demonstrated LC3 conversion and p62 accumulation. D Quantitation of LC3 conversion in CLQ-treated retinas (n = 6). The LC3 II/I ratios of the treated retinas were normalized to those of untreated retinas. An increase in induced LC3 conversion was detected in the treated C57BL/6 and rd16 TRB3−/− retinas. We also observed an increase in p62 level in treated and normalized rd16 retinas as compared to C57BL/6 and rd16 TRB3−/− (n = 4–5). E, F The RFP-GFP-LC3 transgene expression in mouse retinas demonstrated the generation of red puncta in the inner segments of photoreceptors. E Images of the retinal sections of C56BL/6, rd16, and rd16 TRB3−/− mice taken with a confocal microscope. F Quantitation of the red puncta cells in the retinal sections of the three groups of mice (n = 5–7). Data are shown as mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001.