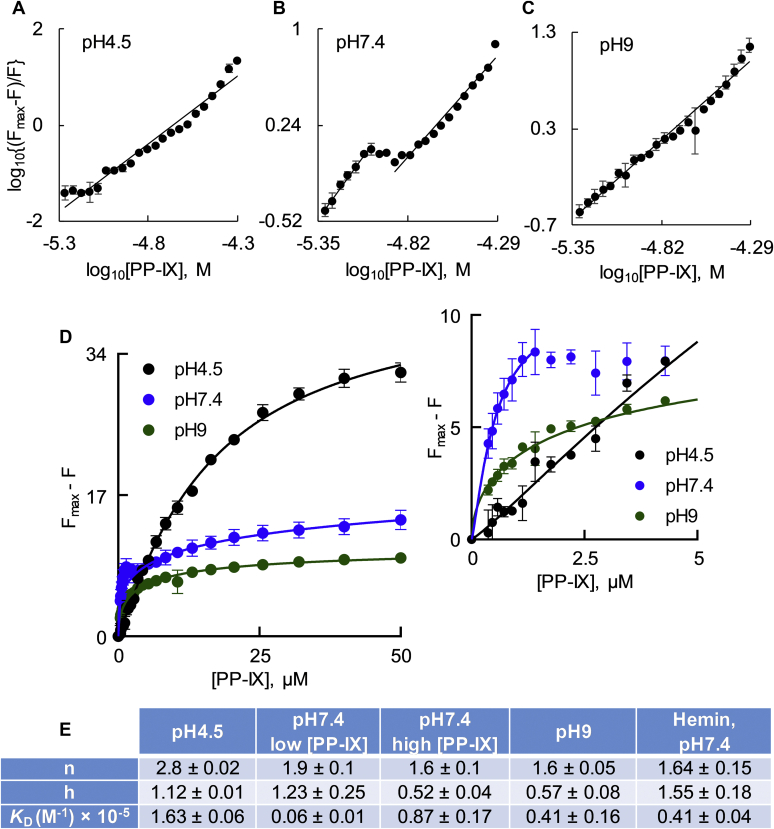
Figure 7.
Fluorescence quenching analyses reveal multiple PP-IX-binding sites on BSA. Increasing PP-IX concentrations (0–50 μM) were incubated with BSA (0.5 μM) for 30 min (pH 4.5, 7.4, 9). After incubation, quenching of the intrinsic BSA fluorescence was analyzed by measuring BSA florescence emission at 347 nm after exciting at 280 nm. A–C, double log plot of log10[(Fmax-F)/F] versus log10[PP-IX], at the indicated pH. D, plot of BSA’s Fmax-F as a function of PP-IX concentration. The smooth lines show the fitting of the data to a nonlinear regression model of saturation binding—“specific binding with Hill Slope” equation in GraphPad Prism 8. The inset of panel D shows a zoomed portion of the initial part of the curve in order to highlight the binding profile from 0 to 5 μM PP-IX. The data is the average of three independent experiments ± standard deviation. E, binding parameters for BSA+PP-IX and BSA+hemin complexes. n, number of binding sites; h, Hill slope; KD, dissociation constant. Data shown are average of three independent experiments ± standard deviation.