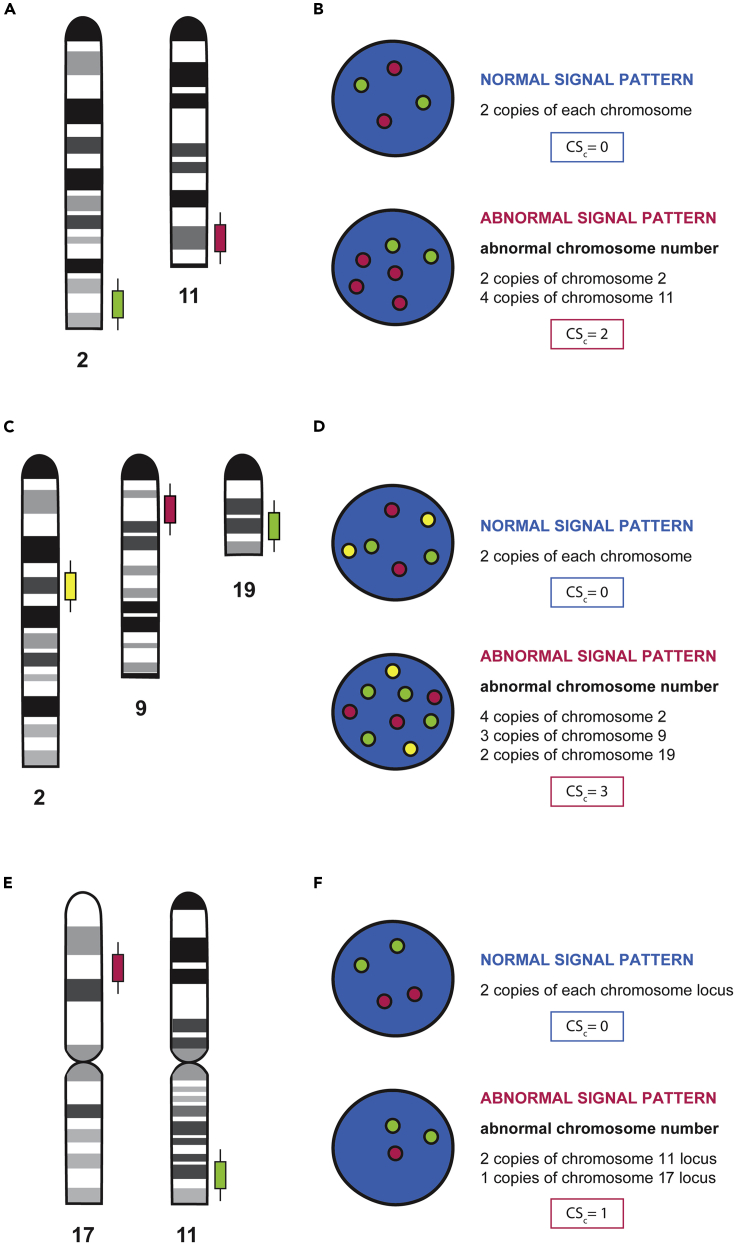
Figure 8.
Probe hybridization and FISH signaling pattern
(A) Schematic representation at genomic level of probe hybridization for the detection of chromosomal aberrations in chromosomes 2 and 11.
(B) Schematic representation of fluorescent probe visualization in interphase nucleus after FISH assay, where the green signal corresponds to chromosome 2 and the red signal corresponds to 11. From top to bottom, the first nuclei represent a control diploid cell with two copies of each chromosome (two red signals, and two green signals). The second nuclei represent an abnormal signaling pattern where chromosome aneuploidy can be visualized (two green signals and four red signals).
(C) Schematic representation at genomic level of probes hybridization for the detection of chromosomal aberrations, in chromosomes 2, 9 and 19.
(D) Schematic representation of fluorescent probe visualization in interphase nucleus after FISH assay, where the yellow signal corresponds to chromosome 2, the red signal corresponds to chromosome 9, and the green signal corresponds to chromosome 19. From top to bottom, the first nuclei represent a control diploid cell with two copies of each chromosome (two yellow signals, two red signals, and two green signals). The second nuclei represent an abnormal signaling pattern where chromosome aneuploidy can be visualized (four yellow signals, three red signals two green signals and).
(E) Schematic representation at genomic level of probes hybridization for the detection of chromosomal aberrations, in chromosomes 17 and 11.
(F) Schematic representation of fluorescent probe visualization in interphase nucleus after FISH assay, where the red signal corresponds to a specific locus of chromosome 17 and the green signal corresponds to a specific locus of chromosome 11. From top to bottom, the first nuclei represent a control diploid cell with two copies of each chromosome locus (two red signals, and two green signals). The second nuclei represent an abnormal signaling pattern where the deletion of the analyzed locus can be visualized (two green signals and four red signals). (B, D, and F) Calculations for CSc score are represented in blue squares (normal signal pattern) and red squares (abnormal signal pattern), for each represented example.