Figure 1.
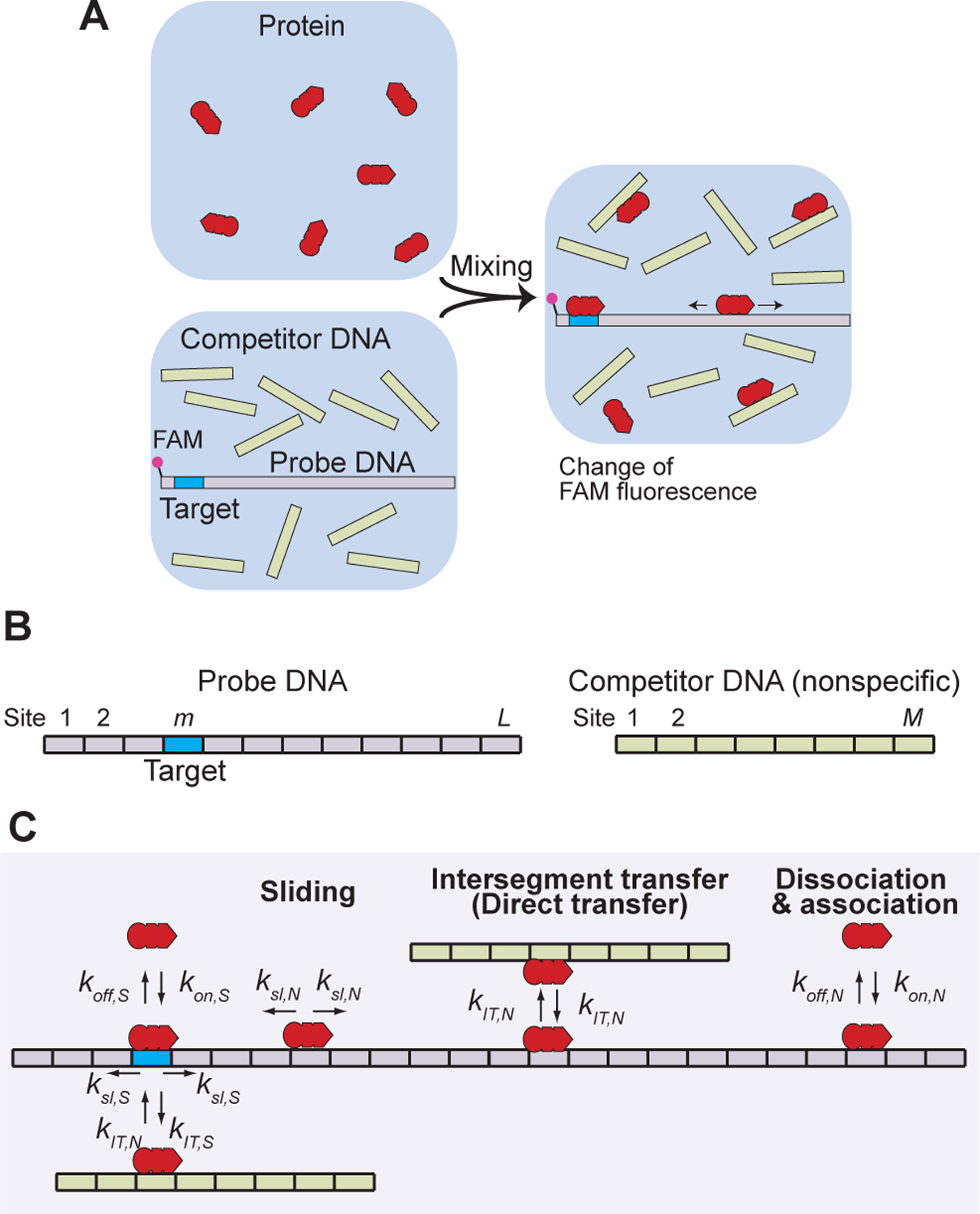
Experimental design and kinetic model used in this study. (A) Stopped-flow fluorescence assay of the target DNA search kinetics. (B) Discrete binding sites on the probe and competitor DNA duplexes. (C) Rate constants involved in our kinetic model for the target association process. The rate constants ksl,N and ksl,S for sliding and the rate constants koff,N and koff,S for dissociation are first-order rate constants (units, s−1), whereas the rate constants kIT,N and kIT,S for intersegment transfer and the rate constants kon,N and kon,S for association are second-order rate constants (units, M−1 s−1). A rate constant for sliding is defined for sliding from one site to an adjacent site (i.e., shift by 1 bp). The rate constant ksl,N is related to the one-dimensional diffusion coefficient D1 for sliding, as indicated by Eq. 15. A complete set of rate equations for this kinetic model is given in the Supplemental Information.
