Figure 1.
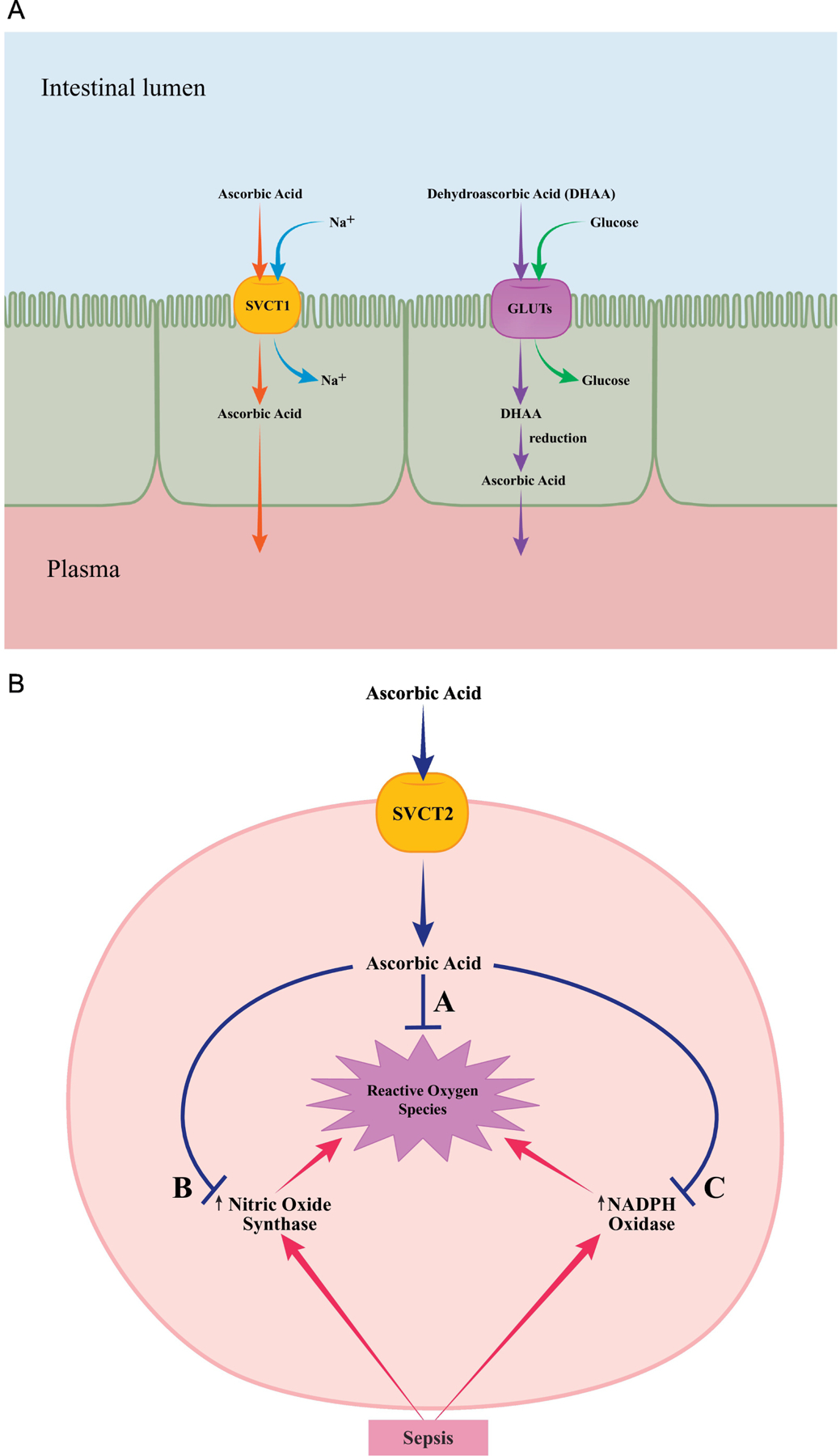
A: Transport of vitamin C
Ingested ascorbic acid is actively transported from the intestinal lumen into cells through sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter 1 (SVCT1) found in small bowel epithelial cells. Dehydroascorbic acid (DHAA) uptake is carried out by facilitated diffusion through glucose transporters (GLUTs). DHAA is then reduced to ascorbic acid intracellularly. Ascorbic acid is ultimately transported into the plasma from the epithelial cells by diffusion.
B: Vitamin C as an antioxidant
Sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter 2 (SVCT2) is responsible for non-epithelial cell uptake and delivery of ascorbic acid in tissues of the brain, eye, bone, heart, lung, adrenal gland and skeletal muscle. Ascorbic acid scavenges reactive oxygen species (A) and diminishes free radical formation by nitric oxide synthase (B) and NADPH oxidase (C) that are activated in response to sepsis.
