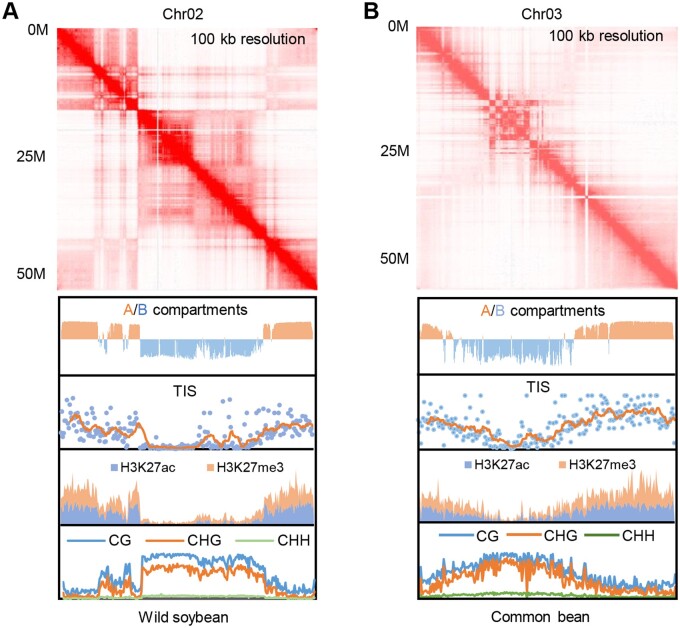
Figure.
Genome architecture evolution between wild soybean (G. soja) and common bean (P. vulgaris). Genome-wide chromosome capture maps (Hi-C) and profiling of chromatin accessibility (displayed as Tn5 transposon insertion sites), histone post-translational marks (H3K27ac, and H3K27me3) and DNA methylation revealed the compartmentalization and features of wild soybean (A) and common bean (B). Data for Chromosomes 2 and 3 are shown. Adapted from Wang et al. (2021); Supplemental Figure S2.