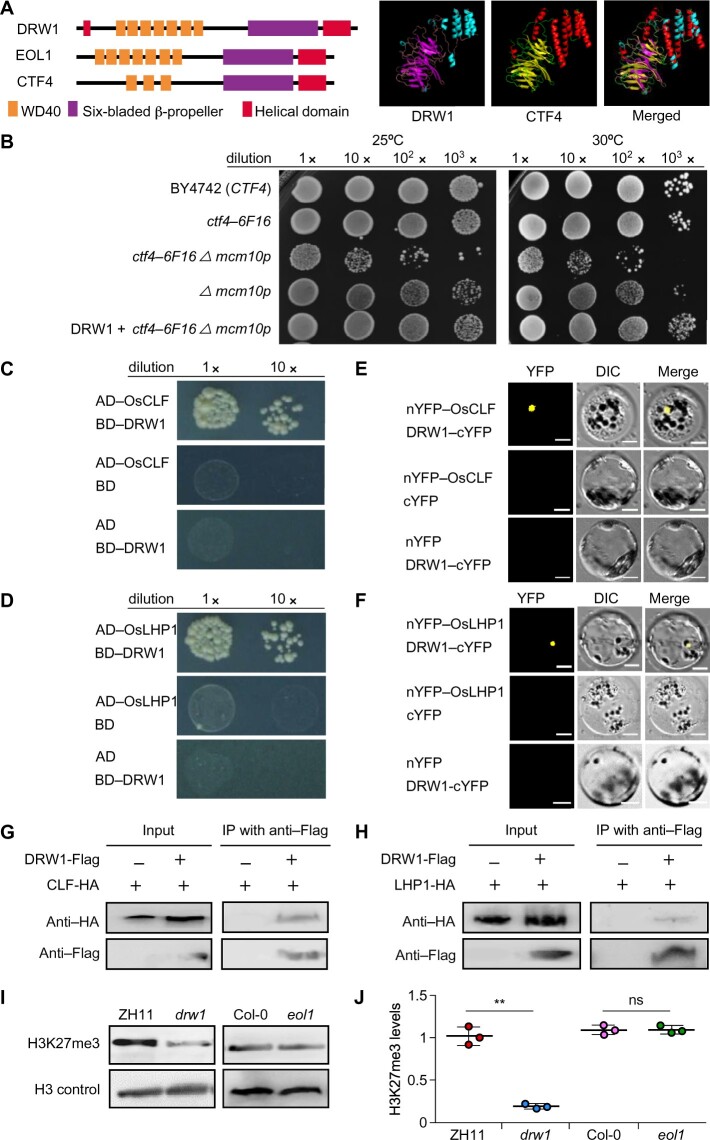
Figure 1.
The CTF4-ortholog DRW1 directly interacts with PRC2 and PRC1 components and mediates H3K27me3 in rice. (A) Domain distribution of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CTF4, Arabidopsis thaliana EOL1, and Oryza sativa DRW1 (left). Homology-modeling-based structural prediction of the DRW1 and CTF4 proteins (right); the structures were merged to help identify differences. (B) Yeast complementation assays showing that expression of DRW1 can complement the growth of the ctf4-6F16 Δmcm10-1 double mutant. Ten-fold serial dilutions of log-phase yeast cells (wild-type, ctf4-6F16Δ, ctf4-6F16 Δmcm10-1, mcm10-1, and DRW1+ctf4-6F16 Δmcm10-1) were spotted onto YPD plates and incubated at both 25°C and 30°C for 3–4 days. (C–D) Y2H analysis showing that DRW1 physically associates with OsCLF (C) and OsLHP1 (D) in yeast cells. Full-length DRW1 and OsCLF or OsLHP1 were fused with the GAL4-AD or GAL4-BD domains (as indicated), and were then transformed into yeast cells and grown on SD (–WLHA) selective medium without tryptophan (W), leucine (L), histidine (H), or adenine (A). (E–F) BiFC analysis of the physical interaction of DRW1 with OsCLF (E) and OsLHP1 (F) in rice protoplasts. Yellow fluorescence signals indicate physical associations of interacting partner proteins in nuclei. EYFP fluorescence was observed in rice protoplasts expressing DRW1-cEYFP and nEYFP-OsCLF and in cells expressing DRW1-cEYFP and nEYFP-OsLHP1. Bars represent 20 μm. (G–H) Co-immunoprecipitation assay of DRW1 with OsCLF (G) and OsLHP1 (H) in rice protoplasts. Total protein extracts of protoplasts prepared from transformed double hemizygous DRW1:FLAG and LHP1:HA cells; these were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG agarose. Subsequently, the precipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti-HA antibody to identify OsCLF:HA and OsLHP1:HA. (I) Loss-of-function DRW1 leads to a decrease in H3K27me3 abundance in rice. Histones derived from 9-day-old seedlings of wild-type ZH11 and drw1 mutant in rice, and wild-type Col-0 and eol1 mutant Arabidopsis plants, were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies specifically recognizing H3K27me3 modification; the anti-H3 antibody was used as a control. (J) Quantitative analysis of the H3K27me3 level in rice drw1 and Arabidopsis eol1 mutants. Signal intensity was quantified using ImageJ. Data are means ± SD, and n = 3 in (H). Student’s two-tailed t test (**, p < 0.01; n.s., not significant).