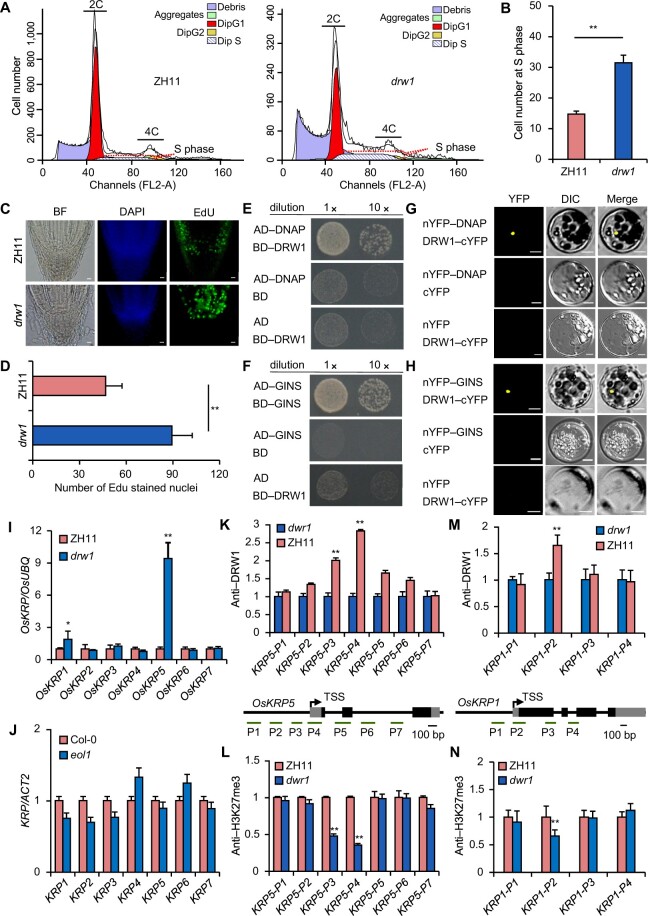
Figure 3.
Loss-of-function DRW1 delays the cell cycle, and DRW1 regulates cell-cycle-related KRP family genes by promoting H3K27me3 deposition at KRP loci. (A) Cell number during cell cycle phases in ZH11 and drw1 measured by flow cytometry assays. (B) Quantitative analysis of cell number at S stage in ZH11 and drw1 plants. (C–D) Quantitative analysis of EDU treatments on the root meristems of 3- to 5-day-old ZH11 and drw1 seedlings. Bar represents 10 μm. (E–F) DRW1 associates with DNAP (E) and GINS (F) in yeast cells. The full-length DRW1 and DNAP or GINS was fused with the GAL4-AD or BD domain (as indicated), and then transformed into yeast cell grown on SD (–WLHA) selective medium without tryptophan (W), leucine (L), histidine (H), or adenine (A). (G–H) BiFC analysis of the physical interaction of DRW1 with DNAP (G) or GINS (H) in rice protoplasts. Yellow signals indicate physical associations of paired proteins in the nuclei. EYFP fluorescence was observed in rice protoplasts fused with constructs separately encoding nEYFP-DNAP or nEYFP-GINS and DRW1-cEYFP. Bar represents 20 μm. (I–J) RT-qPCR detection of expression of KRP family transcripts in rice (I) and Arabidopsis (J). (K–L) ChIP analysis of DRW1 at the OsKRP5 (K) and OsKRP1 (L) loci. Diagram of the OsKRP5 or OsKRP1 loci (below); the transcribed regions are represented by black boxes, and untranslated regions are represented by gray boxes. Positions of the TSS and the binding regions for the primers used in the ChIP experiments are indicated. (M–N) ChIP analysis of H3K27me3 on the OsKRP5 (M) and OsKRP1 (N) loci. Immunoprecipitated genomic fragments were quantified by qPCR. Data are means ± SD, and n = 3 in (B), (D), and (I–N). Student’s two-tailed t test (**, p < 0.01).