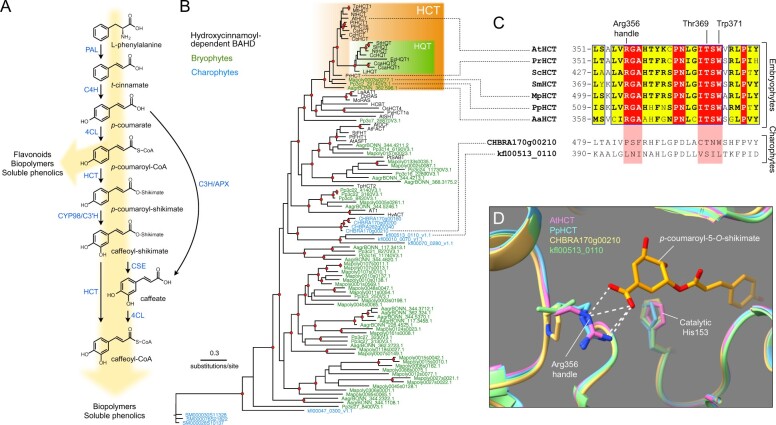
Figure 1.
Evolutionary history of the HCT gene family. A, Schematic representation of the phenylpropanoid pathway of angiosperms leading to caffeoyl-CoA. Enzyme names are indicated in blue. PAL, phenylalanine ammonia lyase; C4H, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase; 4CL, 4-coumarate:CoA ligase; HCT, hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA:shikimate hydroxycinnamoyl transferase; C3′H, p-coumaroyl ester 3′hydroxylase; CSE, caffeoyl-shikimate esterase; C3H/APX, p-coumarate 3-hydroxylase/ascorbate peroxidase. B, Unrooted protein tree describing the phylogenetic relationships between 34 hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA-dependent BAHD acyltransferases of known biochemical function and all BAHDs from K. nitens, C. braunii, S. muscicola, P. patens, M. polymorpha, and A. agrestis. The tree is drawn to scale. Red dots indicate a maximum-likelihood ratio test branch support ≧ 0.80. Lists of characterized and uncharacterized BAHD proteins are available in Supplemental Tables S1, S2, respectively. C, Multiple sequence alignment highlighting the region comprising the three residues controlling shikimate acylation in selected HCT orthologs from the five major embryophyte groups. Corresponding regions from charophyte HCT homologs are displayed at the bottom for comparison. ScHCT, Salvinia cucullata Sacu_v1.1_s0010.g004618; SmHCT, Selaginella moellendorffii 152997. Red box/white character, strict identity; yellow box/black bold character, in-group similarity score >0.7; blue frame/yellow box, cross-group similarity score >0.7. D, Overlay of protein three-dimensional structures depicting the Arg356 handle interaction with shikimate. Models of P. patens (PpHCT, Pp3c2_29140, blue), C. braunii (CHBRA170g00210, yellow), and K. nitens (kfl00513_0110, green) HCT homologs were reconstructed using the crystal structure of AtHCT in complex with p-coumaroyl-5-O-shikimate (PDB entry: 5kju; pink). Residues are numbered according to AtHCT. White dashed lines represent predicted hydrogen bonds