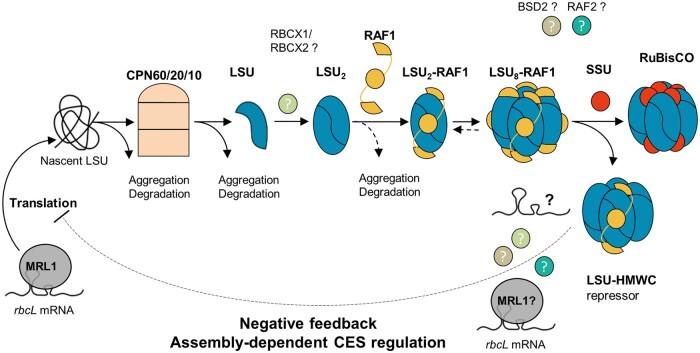
Figure 12.
Model of Rubisco biogenesis pathway and CES regulation. The rbcL mRNA, stabilized by the binding of the MRL1 PPR-protein to its 5′UTR region, can be translated. Nascent LSU is recruited by the chloroplast folding machinery. LSU propeptide is subsequently folded in the CPN60/20/10 chaperonin complex. The released LSU dimerizes, maybe with help of RBCX, and recruits RAF1 which is required for LSU2 stabilization. LSU2-RAF1 unit oligomerizes further to form Rubisco catalytic core. RAF1 is finally substituted by the SSU to form the complete holoenzyme. In the SSU-limiting context, the LSU-RAF1 HMWC is converting to a repressor of rbcL translation (CES process) preventing LSU wasteful production, by binding either directly rbcL mRNA or other factors, thereby displacing some RAF1 oligomers. Many aspects of this model remain unclear such as the identity of the proteins/RNA in the LSU regulator complex, or the exact role of the other Rubisco assembly chaperones such as RBCX1/2 and RAF2, or the presence of a functional homolog of the plant BSD2 factor in algae, which remains debated.