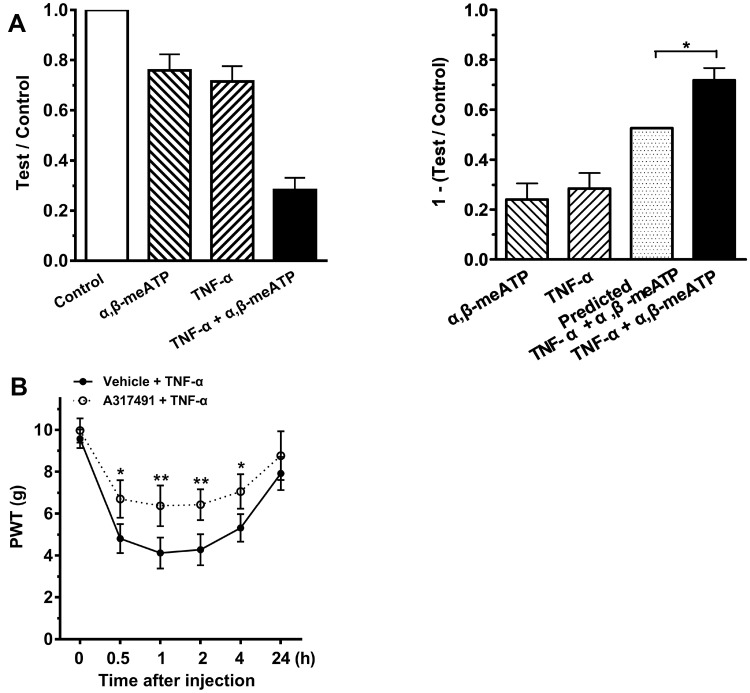
Figure 5.
P2X3 receptors participated in TNF-α-induced mechanical allodynia. (A) Intraplantar individual injection of α,β-meATP (1 nmol in 50 μL) and TNF-α (0.1 ng in 50 μL) produced a moderate decrease in the mechanical threshold (1-test/control). However, a co-injection of α,β-meATP and TNF-α (TNF-α + α,β-meATP) produced a much large decrease in the threshold than adding the threshold reduction caused by TNF-α and α,β-meATP alone (predicted TNF-α + α,β-meATP). Paw withdrawal threshold (PWT) was tested at 15 min after intraplantar injection. PWT was normalized to the baseline values before every injection. n = 10 rats in each group. * P < 0.05, Two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test. (B) After intraplantar injection of TNF-α (1 ng in 50 μL), PWT (in g) significantly decreased at 0.5, 1, 2 and 4 h and recovered at 24 h. The decrease of PWT induced by TNF-α was significantly attenuated when A-317491 (10 nmol in 50 μL), a specific P2X3 receptor antagonist, was pretreated to ipsilateral hind paws. n = 10 rats in each group. *P < 0.05, **p < 0.01, Bonferroni’s post hoc test, compared with vehicle + TNF-α group.