Figure 3. Analysis of in vitro bacterial biofilm formation on an abiotic surface in the presence or absence of lactoferrin.
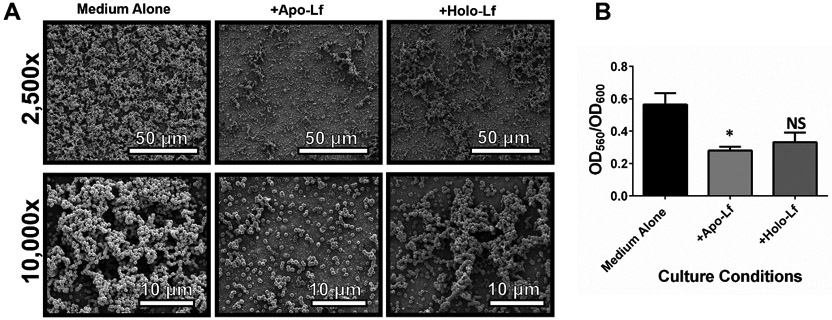
GBS was grown in medium alone or medium supplemented with 250 μg/mL of either apo-lactoferrin (apo-Lf) or holo-lactoferrin (holo-Lf). Bacterial biofilm was analyzed by A) high-resolution scanning electron microscopy (SEM) at low magnification (2,500x, magnification bar indicates 50 μm) and high magnification (10,000x, magnification bar indicates 10 μm) and by B) quantitative analysis of crystal violet staining at an optical density of 560 nm (OD560) normalized to bacterial cell density (OD600). Bars indicate mean values of at least three biological replicates +/−SEM. *P<0.05, Student’s t test comparison to bacteria grown in medium alone. Apo-lactoferrin significantly inhibits GBS biofilm formation, while holo-lactoferrin has an intermediate phenotype that is statistically indistinguishable from the negative control.
