Figure 3. A conserved amphipathic α-helix in WNK1 binds to unassembled EMC2.
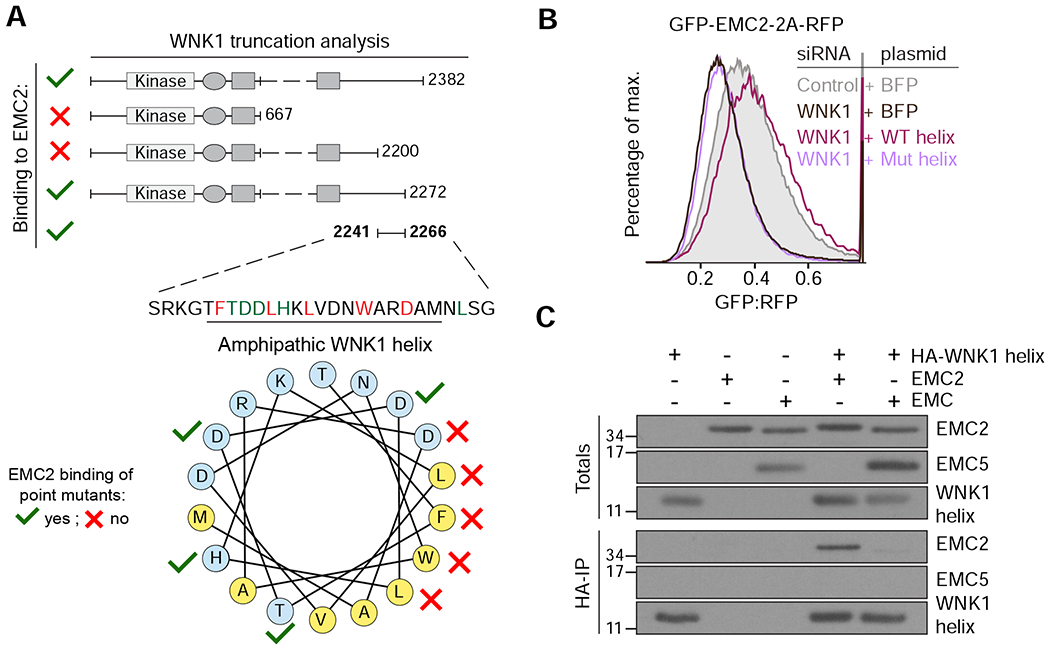
(A) FLAG-tagged WNK1 and its truncations were tested for binding to EMC2 (see methods). The EMC2 binding site was mapped to a previously uncharacterized C-terminal peptide that is predicted to form a conserved amphipathic α-helix (see Figure S4A). Polar residues are shown in blue and hydrophobic residues in yellow. A mutational analysis (Figure S4C) revealed residues required for EMC2 interaction (depicted with red crosses). (B) HEK293T cells stably expressing GFP-EMC2 were transiently transfected with plasmids encoding either BFP or BFP-tagged wild type (WT) or L2250K mutant (Mut) WNK1 helix. Cells were treated with either scrambled or WNK1 siRNA and BFP-positive cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) Intact EMC, purified from stable EMC5-3xFLAG HEK293T cells, and recombinant EMC2 were incubated with 3xHA-tagged WNK1 helix and immunoprecipitated with anti-HA resin. Totals and eluates were analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies.
