FIGURE 1.
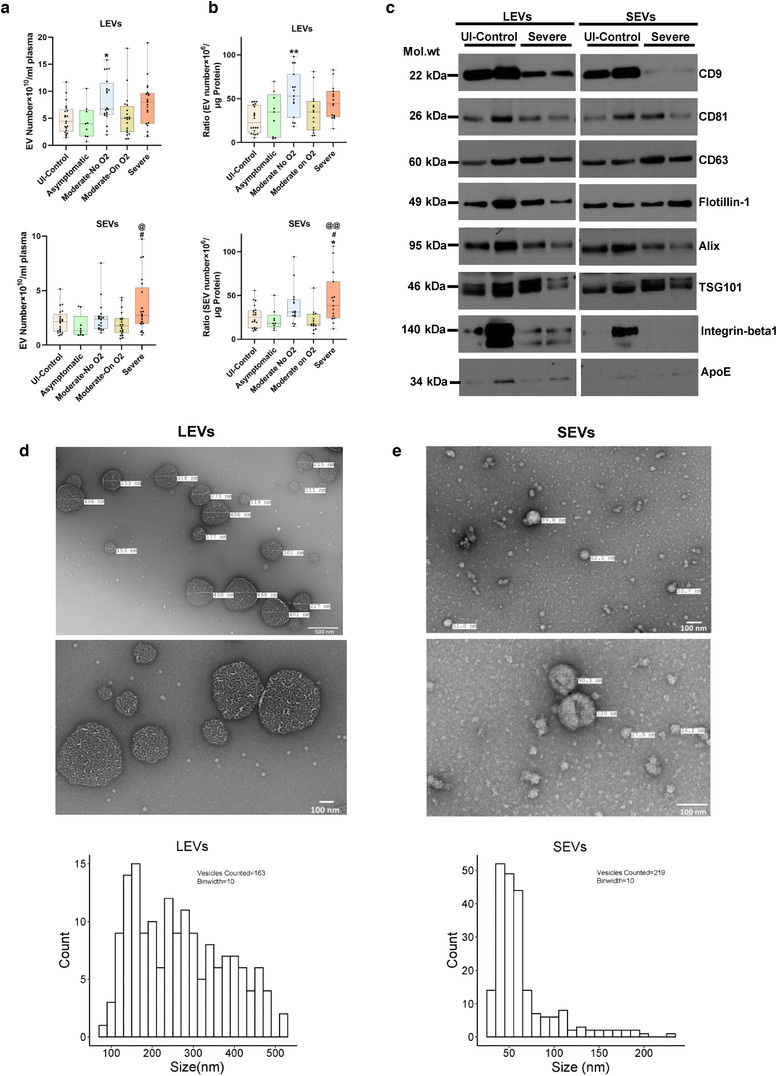
Characterization of extracellular vesicles isolated from plasma of COVID‐19 infected and uninfected individuals. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) were isolated from 1.0 ml of platelet free EDTA‐plasma from Uninfected controls (n = 21), Asymptomatic (n = 9), Moderate‐No O2 (n = 20), Moderate‐On O2 (n = 20) and Severe (n = 21) group COVID‐19 patients by centrifuging at 20,000 g for 15 min (20K pellet large EVs) followed by ultracentrifugation twice at 100,000 g for 70 min (100K pellet small EVs). a) Total large EVs (LEVs, top panel) and small EVs (SEVs, bottom panel) in each group based on nanoparticle tracking analysis. Data represents number of EVs/ml of final EV suspension obtained from 1 ml of EDTA plasma. b) EV to protein ratio in each group Uninfected Control (n = 20), Asymptomatic (n = 9), Moderate‐No O2 (n = 15), Moderate‐On O2 (n = 15), Severe (n = 15). c) Western blot analysis of EV markers in LEVs and SEVs from un‐infected controls (n = 2) and Severe COVID‐19 (n = 2) patients. d‐e) Representative images and particle size distribution of LEVs (d) and SEVs (e) based on Transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Approximately 10–15 TEM images of LEVs and SEVs each were counted using the Image J software. Box plots depicts median and IQR and whiskers represent minimum to maximum points. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 vs UI‐Control, # P < 0.05 vs. Asymptomatic, @ P < 0.05, @@ P < 0.01 vs Moderate‐On O2
