FIGURE 7.
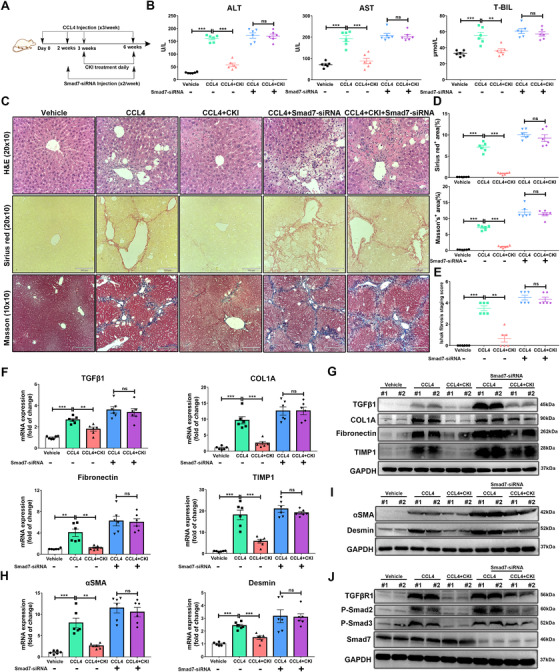
CKI attenuates chronic liver fibrosis through targeting Smad7 in HSCs. (A) Scheme of experimental procedure for C57BL/6 mice intraperitoneally treated with 4 ml/kg CCl4 in olive oil for 6 weeks. Mice were intraperitoneally administrated with CKI (7.5 ml/kg) for 3 weeks, starting at 3 weeks post initiation of CCl4 challenge. Mice were treated with Smad7‐siRNA (5 mg/kg) through retro‐orbital injection of the venous sinus to knockdown Smad7 expression, starting at 2 weeks post initiation of CCl4 challenge. (B) Serum levels of ALT, AST, and T‐BIL were detected in each indicated group (n = 6). (C) Mice liver sections from CCl4‐induced liver fibrosis models were collected for H&E (original magnification 20 × 10, scale bar 100 μm), Sirius Red (original magnification 20 × 10, scale bar 100 μm), and Masson staining (original magnification 10 × 10, scale bar 210 μm) after the final CKI treatment (n = 6). (D) Positive Sirius Red or Masson staining area were quantified by ImageJ analysis (n = 6). (E) Ishak fibrosis score of the Sirius Red‐stained liver sections (n = 6). (F) mRNA expressions of TGF‐β1, COL1A, Fibronectin, and TIMP1 were analyzed by qRT‐PCR in mouse liver tissues. (G) Western blot assay for detecting the expression of TGF‐β1, COL1A, Fibronectin, and TIMP1 in mouse liver tissue. (H) mRNA expressions of αSMA and desmin were analyzed by qRT‐PCR in the liver tissues from CCl4‐challenged mice. (I) Western blot assay for detecting the expression of αSMA and desmin in mouse liver tissues. (J) Western blot assay for detecting the expression of TGFβR1, p‐Smad2, p‐Smad3, and Smad7 in mouse liver tissues. Data are presented as means ± SEM. ns, p > 0.05; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001
