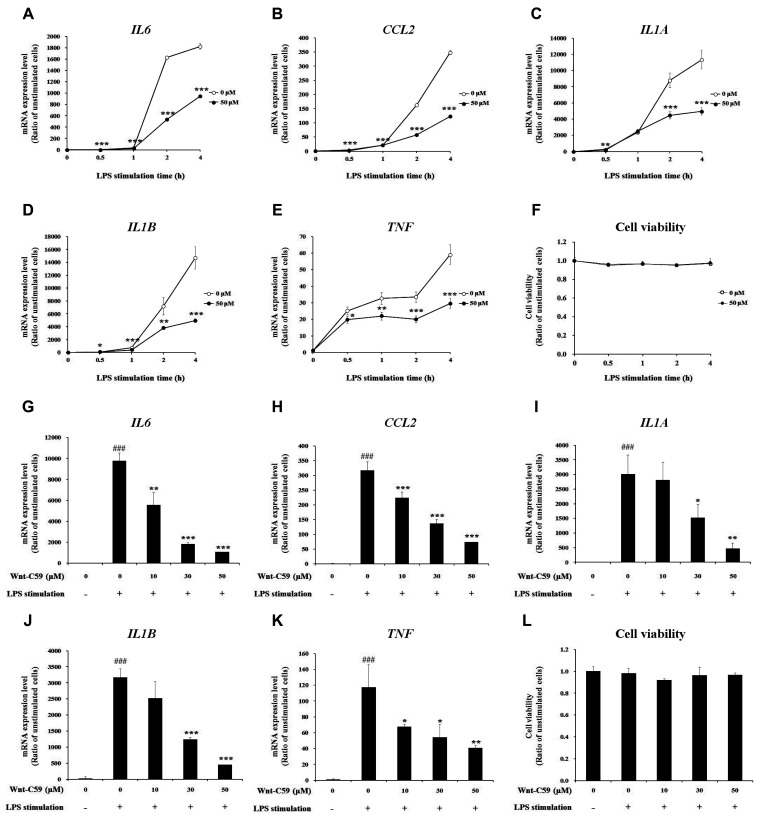
Fig. 2. Suppressive effect of Wnt-C59 on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in RAW264.7 murine macrophage cells.
(A–F) Cells were treated with 0 or 50 μM of Wnt-C59, followed by LPS stimulation at 0.1 μg/ml for various time periods of 0.5 to 4 h. (A–E) Messenger RNA levels of proinflammatory cytokines were measured by RT-qPCR. (F) Cell viability was measured. Cells treated with 0 or 50 μM of Wnt-C59 with the same time period of LPS stimulation were compared. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (G–L) Cells were treated with 0 to 50 μM of Wnt-C59, followed by LPS stimulation at 0.1 μg/ml for 4 h. (G–K) Messenger RNA levels of proinflammatory cytokines were measured by RT-qPCR. (L) Cell viability was measured. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared with cells stimulated with LPS with 0 μM of Wnt-C59. ###p < 0.001 compared with unstimulated cells. Experiments were conducted in triplicate. Data are shown as mean ± standard deviation, and statistical significance was measured by unpaired t-test.