Figure 2 .
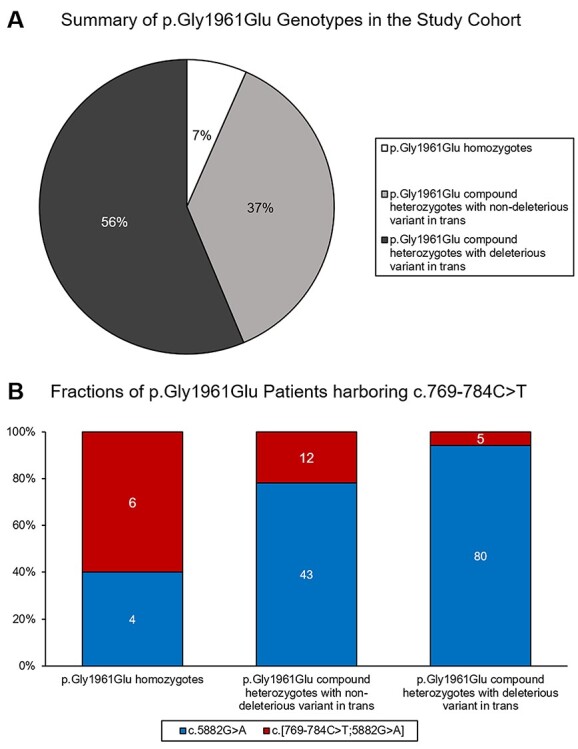
Summary of genotypes in the p.(Gly1961Glu) study cohort. Out of 644 total biallelic patients, 150 (34.7%) harbored the p.(Gly1961Glu) variant. (A) Within this group, 10 (7%) patients were homozygous while the remaining are compound heterozygotes. In more than half of the compound heterozygotes (n = 85, 56%), the mutation in trans was a known or expected (PVS1) deleterious allele as compared to the remaining 56 (37%) compound heterozygotes whose allele in trans is likely ‘non-deleterious’. (B) The deep intronic c.769-784C > T variant was in cis with p.(Gly1961Glu) in 6 out of 10 homozygotes. Among compound heterozygotes, a significantly smaller fraction of those with deleterious alleles in trans had the c.769-784C > T variant on the p.(Gly1961Glu) allele (5.9% vs 21.4% in non-deleterious alleles; FET P = 0.006).
