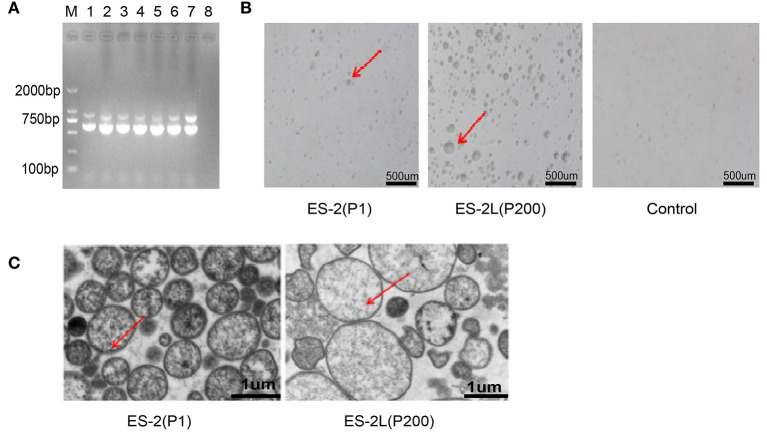
Figure 1.
(A) Detection of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae-specific P36 (948 bp) and 16S RNA (627 bp) genes for the different passage strains: M, DNA marker 2,000; lane 1, ES-2 (P1); lane 2, P40; lane 3, P80; lane 4, P120; lane 5, P160; lane 6, ES-2L (P200); lane 7, positive control; lane 8, negative control. (B) Morphological observation of strain ES-2L and ES-2 on solid medium using a low-power microscope; the colonies of strain ES-2 and ES-2L showed the characteristics of rounded, distinct edges and centers with granules, as indicated by the red arrow. (C) Morphological examination of strains ES-2L and ES-2 observed by transmission electron microscopy, indicating that strain ES-2 had no cell walls, cell membranes were surrounded by capsules, and the cytoplasmic structure was loose; characteristics of strain ES-2L were similar to those of strain ES-2, but there were a few large-celled mutant individuals, as indicated by the red arrow.