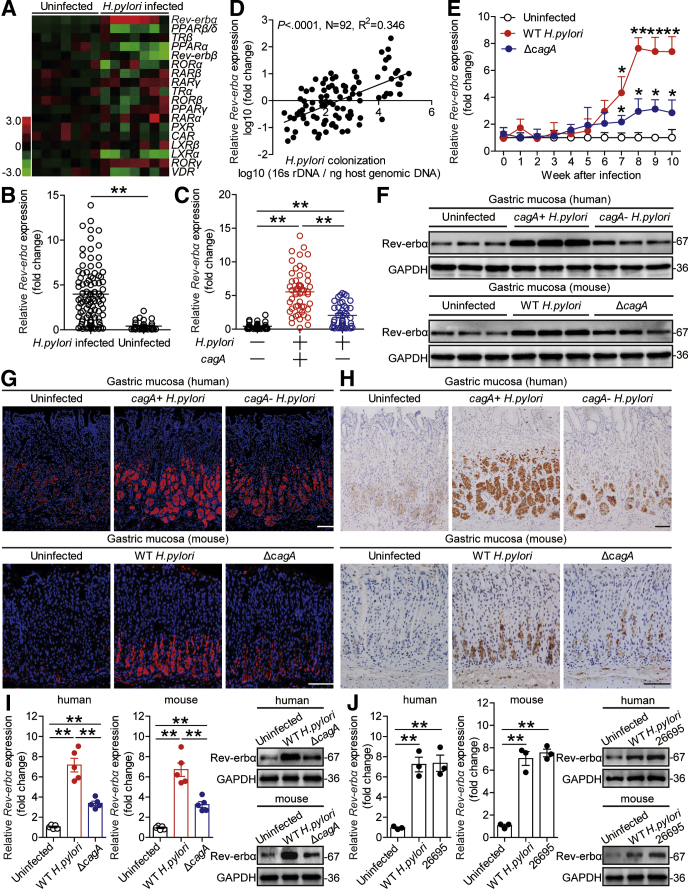
Figure 1.
Rev-erbα is increased in gastric mucosa of H pylori–infected patients and mice. (A) The mRNA expression profiles of thyroid hormone receptor-like superfamily nuclear receptors in human primary gastric mucosa of H pylori–infected patients (n = 7) and uninfected donors (n = 7) was analyzed by real-time PCR. (B) Rev-erbα mRNA expression in gastric mucosa of H pylori–infected (n = 92) and uninfected donors (n = 32) was compared. (C) Rev-erbα mRNA expression in gastric mucosa of cagA+H pylori–infected (n = 51), cagA–H pylori–infected (n = 41), and uninfected donors (n = 32) was compared. (D) The correlation between Rev-erbα mRNA expression and H pylori colonization in gastric mucosa of H pylori–infected patients was analyzed with the Pearson r analyze (R2 = 0.3460, P value < .0001) (E) Dynamic changes of Rev-erbα mRNA expression in gastric mucosa of WT H pylori–infected, ΔcagA–infected, and uninfected mice. n = 5 per group per time point in E. (F–H) Rev-erbα protein in gastric corpus of cagA+H pylori–infected, cagA–H pylori–infected, and uninfected donors or in gastric corpus of WT H pylori–infected, ΔcagA-infected, and uninfected mice 8 weeks p.i. was analyzed by (F) Western blot, (G) immunohistochemical staining, and (H) immunofluorescence staining. Scale bars: 100 μm. (I) Rev-erbα mRNA expression and Rev-erbα protein in human or mouse primary gastric mucosa from uninfected donors infected with WT H pylori or ΔcagA ex vivo analyzed by real-time PCR and Western blot (n = 5). (J) Rev-erbα mRNA expression and Rev-erbα protein in human or mouse primary gastric mucosa from uninfected donors infected with WT H pylori or H pylori 26695 ex vivo analyzed by real-time PCR and Western blot (n = 3). ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01 for groups connected by horizontal lines, or compared with uninfected mice.