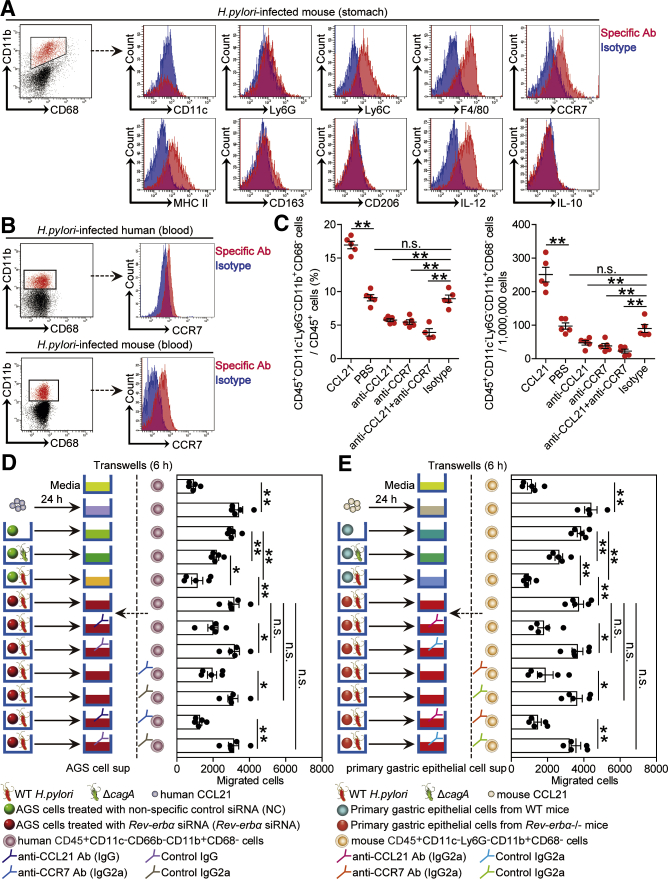
Figure 11.
Rev-erbα inhibits CD45+CD11c–Ly6G–CD11b+CD68–myeloid cell accumulation in vivo and migration in vitro during H pylori infection via CCL21-CCR7 axis. (A) Expression of CD11c, Ly6G, Ly6C, F4/80, CCR7, MHC II, CD163, CD206, IL-12, and IL-10 on/in gastric CD45+CD11c–Ly6G–CD11b+CD68– myeloid cells from WT H pylori–infected WT mice 8 weeks p.i.. Red histograms represent staining of the molecules of interest; blue histograms represent isotype control. (B) Representative dot plots of CCR7 expression on blood CD45+CD11c–CD66b–CD11b+CD68– myeloid cells in blood of H pylori–infected patients or CCR7 expression on CD45+CD11c–Ly6G–CD11b+CD68– myeloid cells of WT H pylori–infected mice 8 weeks p.i.. (C) CD45+CD11c–Ly6G–CD11b+CD68– myeloid cell levels or numbers in gastric mucosa of WT H pylori–infected mice injected with CCL21 or PBS control, or Abs against CCL21 or CCR7 or corresponding isotype control Ab were compared 8 weeks p.i. (n = 5). (D, E) Human CD45+CD11c–CD66b–CD11b+CD68– myeloid cell migration and mouse CD45+CD11c–Ly6G–CD11b+CD68– myeloid cell migration were assessed via a transwell assays as described in the Materials and Methods and statistically analyzed (n = 5). ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01, n.s. P > .05 for groups connected by horizontal lines.