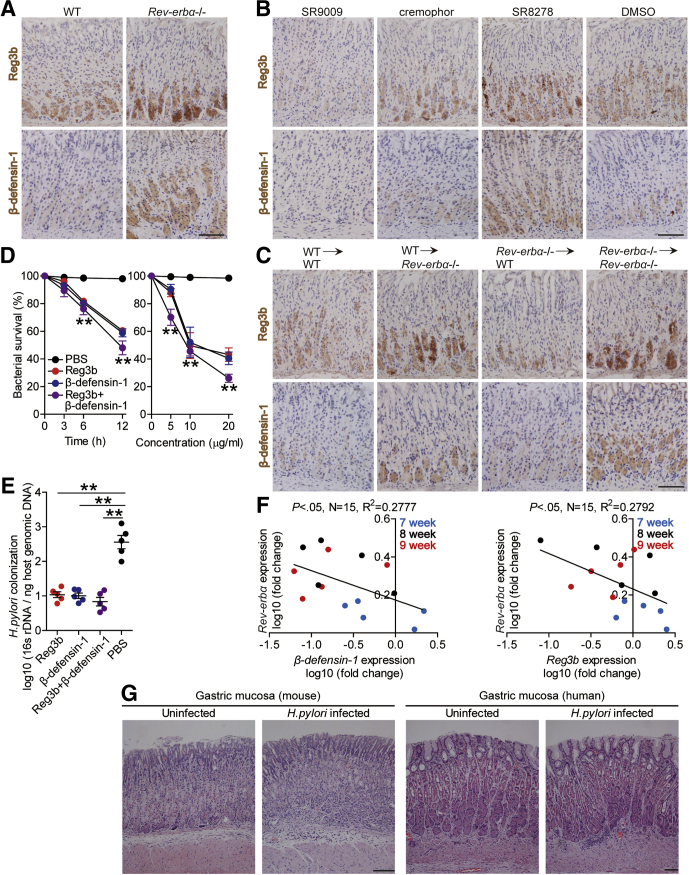
Figure 6.
Antibacterial proteins Reg3b and β-defensin-1 exerted killing activity against H pylori in vitro and in vivo. (A–C) Representative immunohistochemical staining images showing Reg3b or β-defensin-1 expression (brown) in (A) gastric mucosa of WT H pylori–infected WT and Rev-erbα–/– mice, (B) gastric mucosa of WT H pylori–infected mice injected with Rev-erbα agonist SR9009 or cremophor control, or Rev-erbα antagonist SR8278 or DMSO control, or (C) or in gastric mucosa of WT H pylori–infected BM chimera mice 8 weeks p.i.. Scale bars: 100 μm. (D, E) In vitro and in vivo bactericidal assay was performed as described in the Materials and Methods and statistically analyzed (n = 3). (F) The correlation between Rev-erbα expression and Reg3b or β-defensin-1 expression in gastric mucosa of WT H pylori–infected WT mice 7, 8, and 9 weeks p.i. was analyzed with the Pearson r analyzer (R2 = 0.2777 and 0.2792, P value < .05). (G) Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining images showed the histology of gastric mucosa of uninfected and H pylori–infected human and mice. Scale bars: 100 μm. ∗∗P < .01, for groups connected by horizontal lines, or compared with samples treated with PBS.