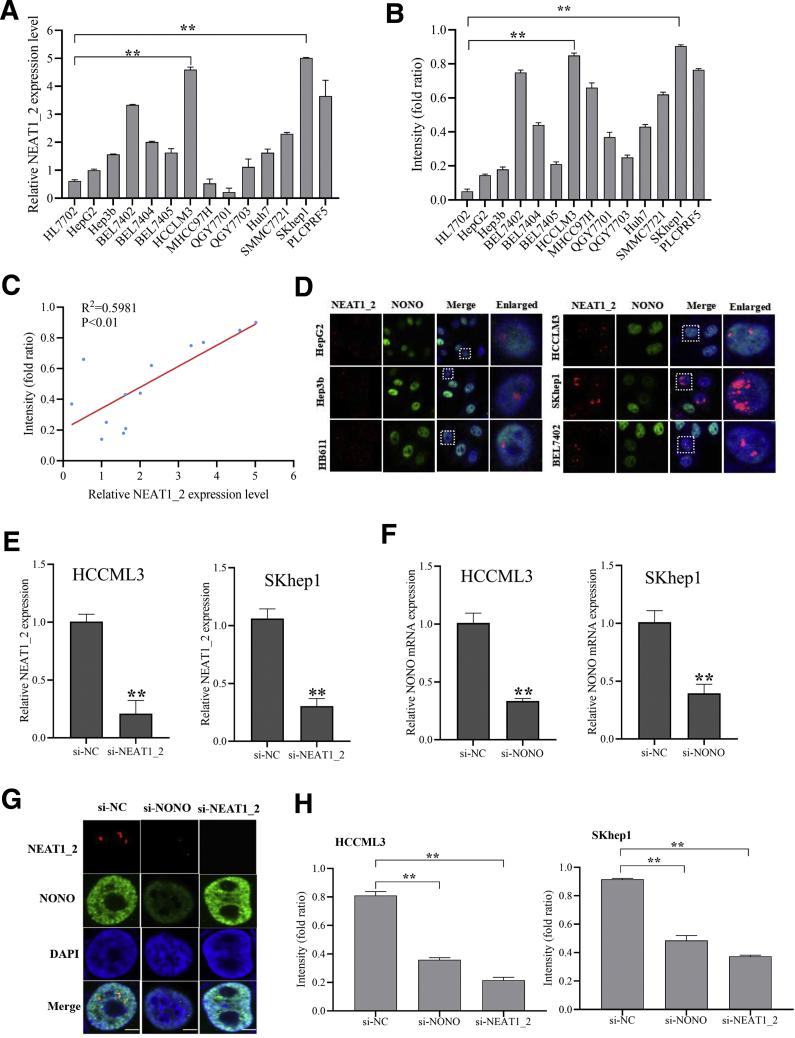
Figure 1.
Paraspeckle in HCC cells is negatively related to T-cell–mediated HCC cell killing effects. (A) Relative expression of NEAT1_2 in the indicated HCC cell lines and human normal liver cell line HL7702 were detected by qRT-PCR. (B) Response of HCC cells and normal liver cells HL7702 to T-cell–mediated cytolysis was detected by T-cell–mediated tumor cell killing assay. (C) Correlation analysis of relative expression of NEAT1_2 in HCC cells and response of HCC cells to T-cell–mediated cytolysis. (D) Cellular distribution of NEAT1_2 and NONO in the indicated HCC cells was detected by FISH and immunofluorescence assay. White scale bar in all images denotes 5 μm. (E) qRT-PCR analysis of knockdown efficacy of NEAT1_2 in HCCLM3 or SKhep1 cells. (F) qRT-PCR analysis of knockdown efficacy of NONO in HCCLM3 or SKhep1 cells. (G) Cellular distribution of NEAT1_2 and NONO in HCCML3 cells transfected with si-NC, si-NEAT1_2, or si-NONO was detected. (H) Response of HCCML3 or SKhep1 cells transfected with si-NC, si-NEAT1_2, or si-NONO to T-cell–mediated cytolysis was detected. Data are represented as means ± standard deviation (SD) (n = 3; ∗P < .05, ∗∗P < .01).