Fig. 4.
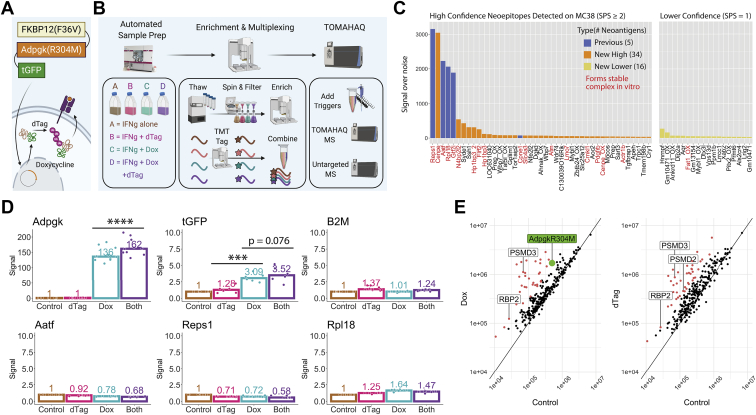
TOMAHAQ detection of neoepitopes in MC38 cells with and without induced expression and/or degradation of the Adpgk(R304M) neoantigen construct idAdpgkG.A, illustration of the inducible expression and degradation construct idAdgpkG, containing an FKBP12(F36V) degron on the N-terminus and turboGFP protein on the C-terminus of the MC38 neoantigen Adpgk(R304M). Upon treatment with doxycycline, the idAdgpkG neoantigen construct is overexpressed. Treatment with dTAG-13 (dTAG) (25) leads to increased ubiquitination and degradation of the neoantigen and a potential increase in presentation of neoantigen-derived MHC-I peptides. Flow cytometry and immunoblot confirm the expected changes on the proteomic level (supplemental Fig. S10). B, scheme showing the idAdpgkG experimental setup. In the first phase, cells were grown and treated using the automated CompacT SelecT cell culture system under −/+ doxycycline, −/+ dTAG conditions in a 20 ng/ml IFNγ background. Next, RNA sequencing and global proteomic analysis were carried out (supplemental Fig. S11), along with MHC-I enrichment and TMT tagging using the AssayMAP Bravo before being combined into a single, multiplexed sample. Finally, NEO223 synthetic triggers were added to the endogenous, multiplexed sample that was then assayed using TOMAHAQ and untargeted mass spectrometry. C, neoepitopes detected on the surface of IFNγ-treated idAdpgkG MC38 cells (no dox or dTAG) using the described MHC-I enrichment, peptide modification, and TOMAHAQ workflow. Target peptides identified using signal over noise (S/N) ≥15 per channel per replicate were separated into high and lower confidence categories, based on the number of MS2 fragment ions selected for MS3 (at least two for high confidence, one for lower confidence). Five previously observed neoantigens were detected with high confidence, along with 34 novel neoantigens with high confidence and 16 with lower confidence. To support the identification of novel neoantigens, the names of peptide–MHC complexes found to form stable complexes in vitro (melting temperatures >40 °C in a DSF assay, data not shown) are colored red. D, TMT-quantified, treatment-specific fold changes in abundance for high interest targets, normalized to 1 for the control condition. Peptides from AdpgkR304M and turboGFP show significantly increased abundance upon dox treatment, and Adpgk(R304M) peptides show a further significant increase upon additional dTAG treatment. Nonconstruct targets, including those derived from ß2M and other neoantigens, do not show an increase upon treatment (see Github repository for data on all targets). E, to determine the specificity of dox and/or dTAG treatment, untargeted MHC-I peptidomics was performed on the same four samples that were assayed using TOMAHAQ. The AdpgkR304M neoepitope was detected in doxycycline-containing conditions only, while both dox and dTAG showed increases in numerous peptides (>3-fold upregulation in red), including E3 ligases and proteasomal subunits (labeled). Units on both axes represent signal intensity.