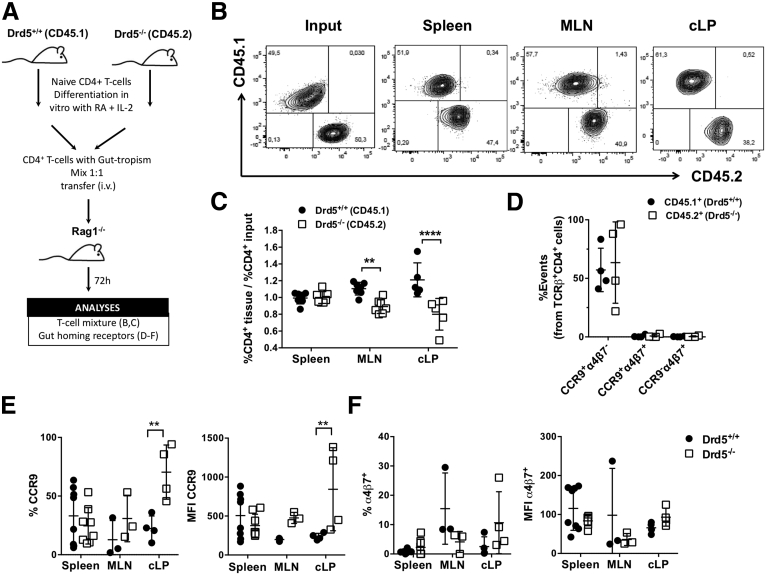
Figure 3.
DRD5 signaling is required for gut homing of CD4+T cells in inflammatory conditions. Naïve CD4+ T cells (CD3+CD4+CD45RBhigh) were isolated from the spleen of Cd45.1+/+Drd5+/+ (black bars) or Cd45.2+/+Drd5–/– (white bars) mice and then activated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 mAbs-coated Dynabeads in the presence of IL-2 and RA for 5d to induce gut tropism. Afterward, CD45.1+ and CD45.2+ cells were mixed in a 1:1 ratio and intravenously injected (2x106 total cells per mouse) into Rag1–/– recipient mice. Mice were sacrificed 72 hours later and the relative composition (CD45.1+ vs CD45.2+) and expression of gut-homing molecules on CD4+ T cells isolated from different tissues was analyzed. (A) Scheme illustrating the experimental design. (B) Representative contour plots analyzing the relative abundance of CD45.1+ vs CD45.2+ CD4+ T cells in the input or infiltrating different tissues. (C) Quantification of the relative abundance of CD45.1+ vs CD45.2+ CD4+ T cells normalized by the input. Data are the % of CD45.1+ or CD45.2+ from CD4+ T cells in a given tissue divided by the % of CD45.1+ or CD45.2+ from CD4+ T cells in the input (n = 7 mice/group). (D–F) CCR9 and α4β7 expression was analyzed in CD45.1+ and CD45.2+ CD4+ T cells isolated from different tissues. (D) Values represent the percentage of CCR9+α4β7–, CCR9+α4β7+, or CCR9–α4β7+ cells in the TCRβ+CD3+CD4+ population from the input (n = 4 mice/group). (E, F) Quantification of the percentage (left panels) and the mean fluorescence intensity (right panels) of (E) CCR9 and (F) α4β7 expressed in CD4+ T cells isolated from the spleen, MLNs, and cLP (n = 3–8 mice/group). (C–F) Each symbol represents data obtained from an individual mouse. Mean ± SD are indicated. ∗∗P < .01; ∗∗∗∗P < .0001 by 2-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s post hoc test.