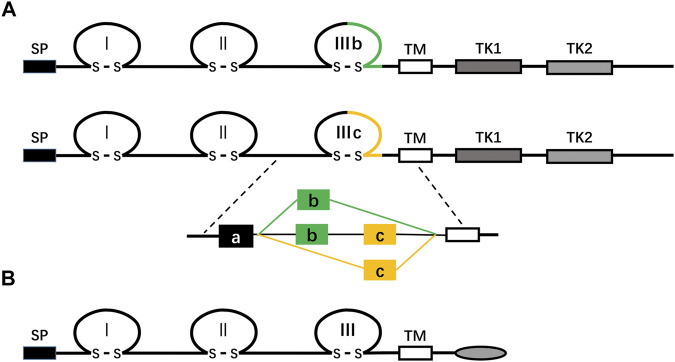
FIGURE 2.
(A) shows a schematic diagram of the protein structure of FGFR. FGFR is a receptor tyrosine kinase composed of about 800 amino acids, with multiple domains, including three extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains (I, II, and III), a transmembrane domain (TM), and two intracellular tyrosine kinase domains (TK1 and TK2). SP represents a cleavable secretory signal sequence. The FGFR gene family consists of four members, FGFR 1–4. Among them, FGFR 1–3 produces two major splicing variants of the immunoglobulin-like domain III, called IIIb and IIIc, which are essential determinants of ligand binding specificity. (B) The schematic representation of the FGFRL1/FGFR5 protein structure is shown. FGFR5, similar to FGFRs in structure, is a membrane protein composed of about 500 amino acids, with three extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains (I, II, and III), a transmembrane domain (TM), and a short cytoplasmic tail without tyrosine kinase domain. SP represents a cleavable secretory signal sequence.