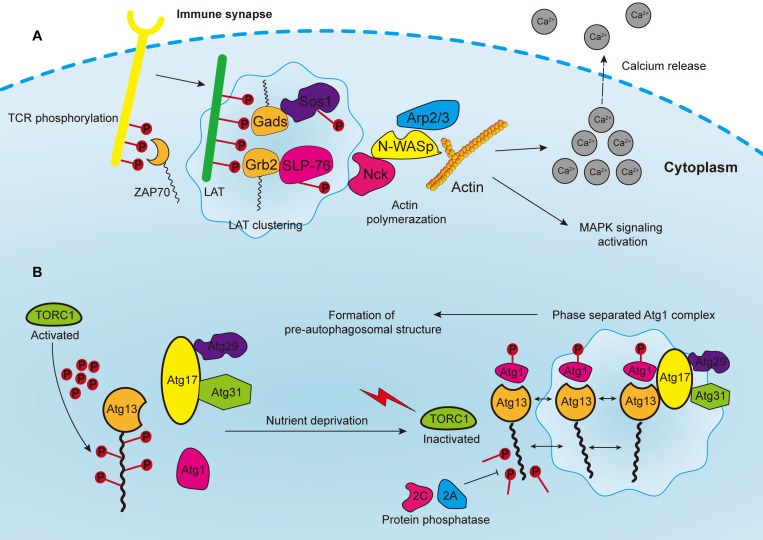
FIGURE 3.
(A) Phosphorylated T cell receptors (TCRs) recruit and activate cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase ZAP70, which in turn phosphorylates the linker for the activation of T cells (LAT). LAT drives the formation of clusters enriched with downstream proteins, such as Gads and Grb2, which recruit adaptor proteins, such as Sos1 and SLP76. Phosphorylated Sos1 and SLP76 initiate the recruitment of actin effectors such as WASP, Nck, and Arp2/3 complex for polymerization of actin filaments, consequently leading to calcium release, MAPK signaling activation, and the formation of an immune synapse. (B) In yeast cells, the Atg1 complex consists of five subunits including Atg1, Atg13, Atg17, Atg29, and Atg31, which are abundant with IDRs for subsequent phase separation. The Atg13 is highly phosphorylated by TORC1 under nutrient replete conditions, leading to the block of Atg1 complex formation. Upon nutrient deprivation, TORC1 is inactivated, and Atg13 is therefore dephosphorylated by protein phosphatases 2C and 2A, whereas Atg1 is auto-phosphorylated. Atg13 serves as a scaffold protein to bind with Atg1 and Atg17-Atg29-Atg31 to promote the phase separation of Atg1 complex, and consequently the formation of pre-autophagosomal structure.