Figure 3 .
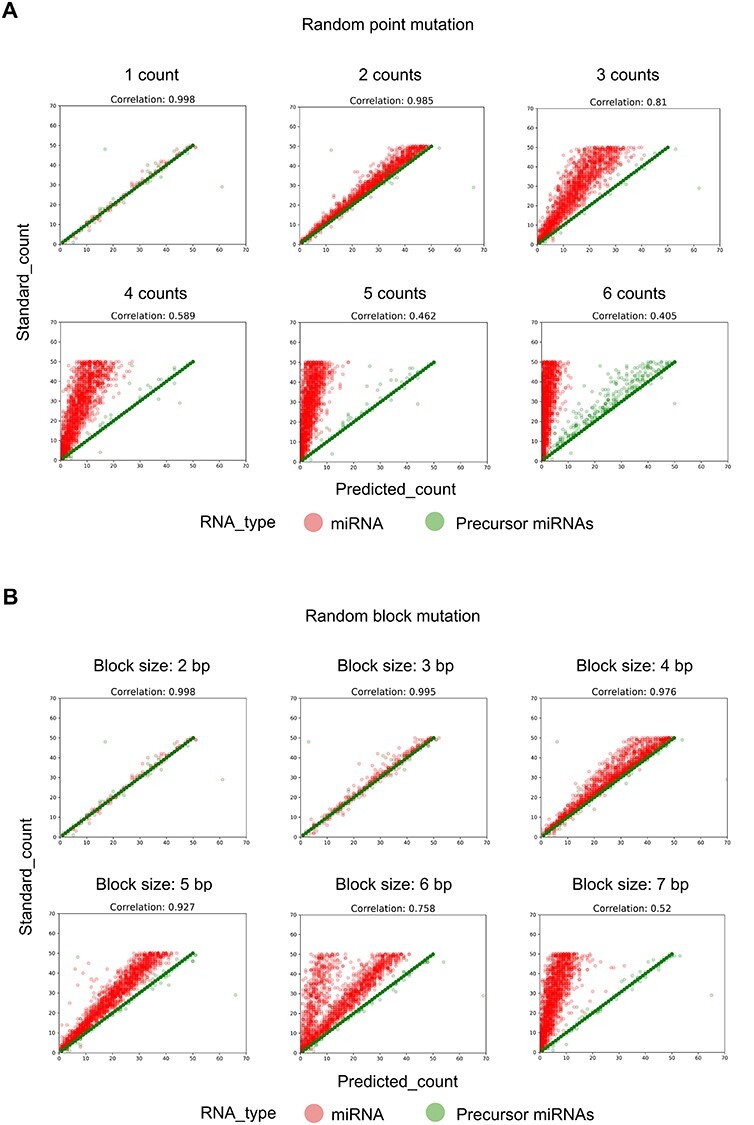
Evaluation of AASRA alignment accuracy in annotating reads with point or block mutations. (A) Random point mutations refer to point mutations randomly assigned to each simulation dataset generated by EMBOSS-msbar. Point mutations include insertion, deletion, mismatch, duplication, and move. Move means the block sequence copied from one region to another (without deletion of the original). Counts represent the number of point mutations in each read. (B) Various types of block mutations randomly assigned to each simulation dataset generated by EMBOSS-msbar. The types of block mutations include insertion, deletion, mismatch, duplication, and move. Block size refers to the length of block mutations in each read. Pearson product–moment correlation coefficients between the standard counts and the annotation software predicted counts are indicated.
