FIGURE 1.
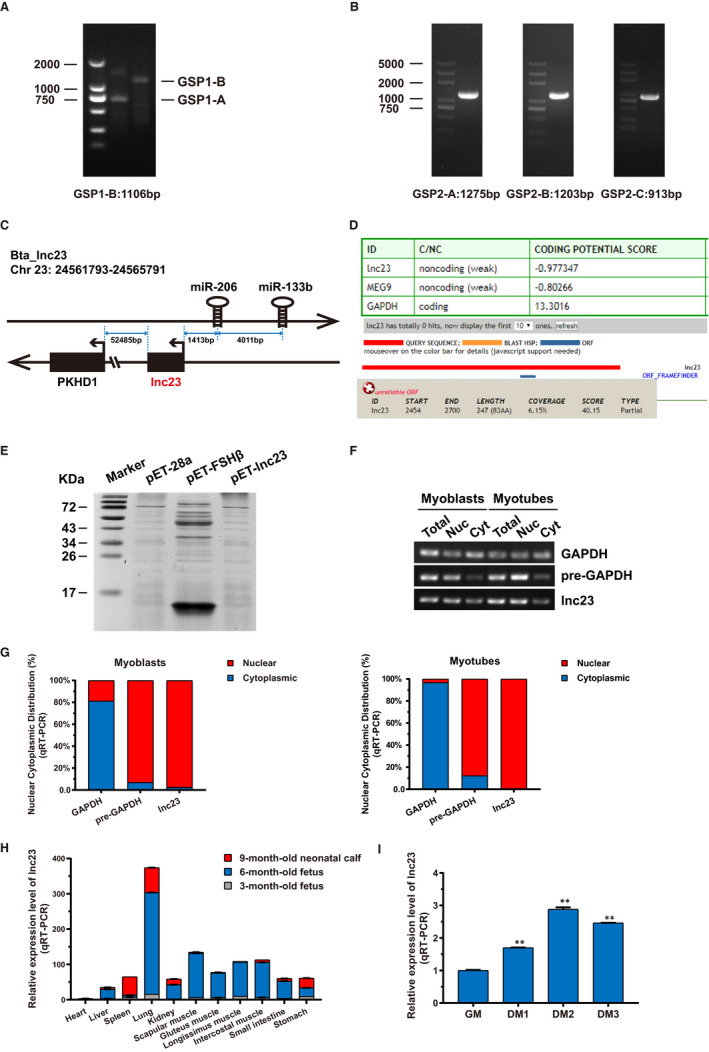
Characterization and expression pattern of lnc23. (A) 5′‐RACE of lnc23 in bovine skeletal muscle cells. GSP1‐A and GSP1‐B are the gene‐specific primers (GSPs) of 5′‐RACE. (B) 3′‐RACE of lnc23 in bovine skeletal muscle cells. GSP2‐A, GSP2‐B and GSP2‐C are the gene‐specific walking primers of 3′‐RACE. (C) Genome localization schematic of lnc23. Lnc23 is located on chromosome 23 of the bovine genome, the upstream genes are miR‐133b and miR‐206, and its downstream gene is PKHD1. (D) Prediction of coding potential using CPC Program. Both lnc23 and MEG9 were predicted to be non‐coding RNA and found that lnc23 had a small open reading frame (ORF), while GAPDH was identified to code for protein. (E) In vitro translation system showed no evidence of protein product from lnc23, while the positive control bovine FSH‐β could encode a ~14 kD protein. (F‐G) The subcellular location of lnc23. Total RNA, nuclear RNA and cytoplasmic RNA were extracted from proliferation cells (Myoblasts) and differentiated cells of 2 d (Myotubes). With the pre‐GAPDH and GAPDH, mRNAs were, respectively, used as nuclear and cytoplasmic iconic gene, the RT‐PCR (F) and qRT‐PCR (G) showed that lnc23 was predominantly located in nucleus. (H) Tissue expression profile of lnc23. The qRT‐PCR was performed to detect the expression of lnc23 in heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, scapular muscle, gluteus muscle, longissimus muscle, intercostal muscle, small intestine and stomach, of which were all from 3‐mo‐old foetus, 6‐mo‐old foetus and 9‐mo‐old neonatal calf. (I) Time series expression profile of lnc23. The bovine myoblasts and myotubes from GM, DM1, DM2 and DM3 were used for detecting lnc23 expression by qRT‐PCR
