FIGURE 2.
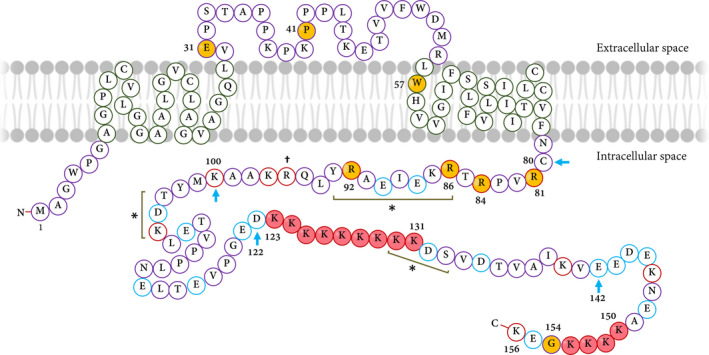
The TMIE protein structure. TMIE consists of an intracellular N‐terminus, two transmembrane parts separated by an extracellular loop and a long‐charged intracellular C‐terminus. The reported mutations are indicated by the yellow‐filled circles. The dagger (†) shows the affected residue in the counterpart of SrJ mouse. The positively charged amino acids are shown by red circles whereas negatively charged residues are indicated by blue ones. There are several lysine (K) residues in C‐terminal that are shown by red‐filled circles. Three potential protein kinase phosphorylation sites are among 86‐93, 103‐105 and 131‐133 residues—are shown by asterisks (*). The potential binding sites for the TMC1/2 proteins are among 80‐100 amino acid positions. Blue arrows highlight the regions that are the target for phosphatidylinositol 4,5‐bisphosphate (PIP2)—residues from 80 to 100 and 122 to 142. The two clusters of lysine (K) residues in the C‐terminal are indicated by red circles (from 123 to 131 and 150 to 154 residues). The figure is depicted according to the amino acid sequence and also data provided by Ref. [113]
