FIGURE 4.
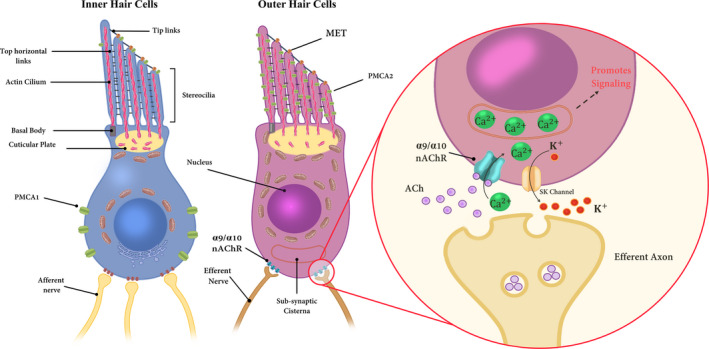
Detailed diagram of the synaptic terminal of afferent and efferent neurons onto outer and inner hair cells. Ca2+ enters via mechanotransducer (MET) channels in the stereocilia of both hair cell types, and also via voltage‐dependent Ca2+ channels (mainly in inner hair cells) and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR) in outer hair cells. The efferent nerve's terminals release acetylcholine (ACh), which activates α9α10 nicotinic receptors (nAChRs) in outer hair cells. Ca2+ influx through these receptors activates SK or potassium (K+) channels (is depicted as a yellow channel). A Ca2+ store is always observed in direct opposition to the location of the nicotinic receptors. Ca2+ can trigger the signalling pathways in the target cell (Hair cells). Two types of Ca2+ ATPase pumps exist in hair cells extruding the Ca2+ including PMCA1 in inner hair cells and PMCA2 in outer hair cells. The figure is redrawn from Ref. [115]
