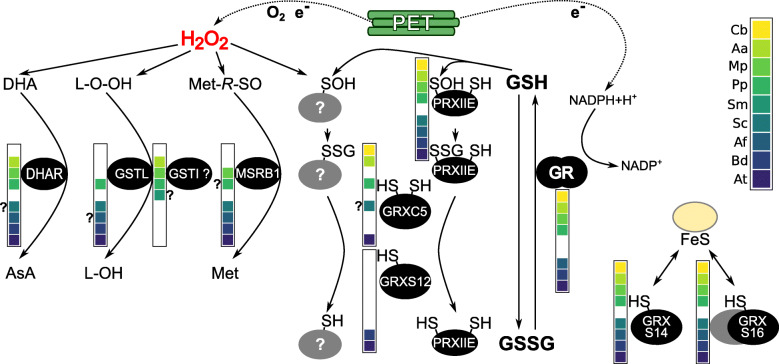
Fig. 2.
Overview of evolution of plastid glutathione-related redox networks in land plants and streptophyte algae. Schematic overview of the plastid GSH-dependent redox network in land plant model species and the streptophyte alga C. braunii. Electrons from photosynthetic electron transport (PET) contribute to ROS generation and at the same time to ROS scavenging, damage repair and redox homeostasis. H2O2 leads to lipid peroxidation (L-O-O-H) as well as oxidation of protein methionine (Met-R-SO), of ascorbic acid (AsA) to dehydroascorbate (DHA) or protein thiol oxidation to the respective sulfenic acid (RS-OH) that can react with GSH to form an S-glutathionylated adduct (RS-SG). Glutaredoxins (GRX) can (de) glutathionylate proteins. The balance between the reduced tripeptide glutathione (GSH) and glutathione disulfide (GSSG) is influenced by GSSG generation via enzymes involved in ROS/RNS scavenging or protein as well as lipid repair, such as dehydroascorbate reductase (DHAR), atypical (1 Cys) methionine sulfoxide reductases B1 (MSRB1), lambda and iota-type (?, function not confirmed in vitro) glutathione S-transferases and type II peroxiredoxins (PRX). Glutathione reductase (GR, NADPH-dependent) safeguards a highly reduced GSH-pool. The presence of at least one plastid-targeted isoform of a protein in a model species (assessed by presence of an N-terminal extension and targeting predictions, see Additional files 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8) is represented by a coloured box in the species legend next to the protein. A coloured box with question mark means the potential presence of an isoform as targeting prediction is unclear, but N-terminal extension indicating a targeting peptide is present (see Additional files 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8). Absence of a box can either mean absence of homologs from that species (see Fig. 1), or that all homologs do not have N-terminal extensions or that gene models are fragmentary (see Additional files 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8). Species legend: Chara braunii (Cb), Anthoceros agrestis (Aa), Marchantia polymorpha (Mp), Physcomitrium patens (Pp), Selaginella moellendorffii (Sm), Salvinia cucullata (Sc), Azolla filiculoides (Af), Brachypodium distachyon (Bd) and Arabidopsis thaliana (At)