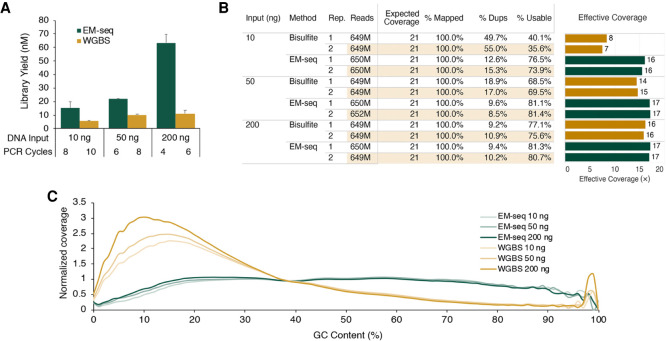
Figure 3.
NA12878 EM-seq libraries. EM-seq and bisulfite libraries were made using 10 ng, 50 ng, or 200 ng of NA12878 DNA (spiked with 2 ng unmethylated lambda DNA and 0.1 ng CpG methylated pUC19). Libraries were sequenced on an Illumina NovaSeq 6000, and 324 million read pairs per library were used for analysis. (A) EM-seq uses fewer PCR cycles but results in more PCR product than does WGBS for all NA12878 input amounts. (B) Table of sequencing and alignment metrics for EM-seq and WGBS libraries using 324 million Illumina read pairs. Metrics were calculated using bwa-meth, SAMtools, and Picard. Theoretical coverage is calculated using the number of bases sequenced/total bases in the GRCh38 reference. (% Mapped) Reads aligned to the reference genome (grch38+controls); (% Dups) reads marked as duplicate by Picard MarkDuplicates; (% Usable) the set of Proper-pair, MapQ 10+, primary, nonduplicate reads used in methylation calling (SAMtools view -F 0xF00 -q 10); and (Effective Coverage) % Usable × theoretical coverage. (C) GC-bias plot for EM-seq and WGBS libraries. EM-seq libraries display an even GC distribution, whereas WGBS libraries have an AT-rich and GC-poor profile.