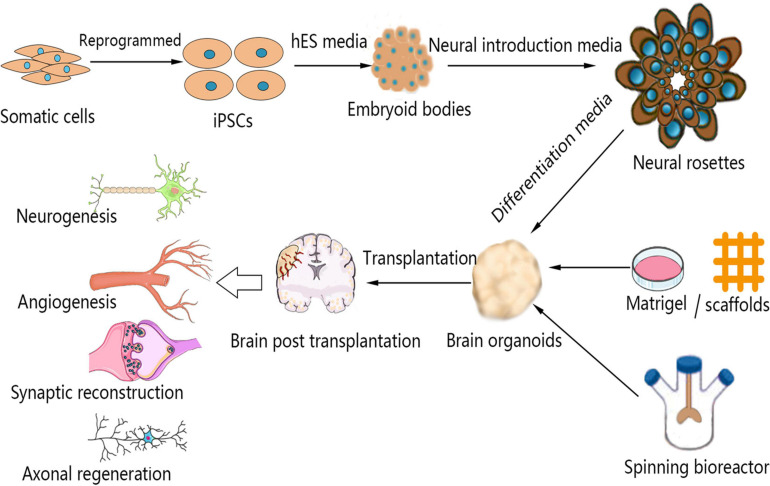
FIGURE 1.
Schematic representation of the brain organoid culture process and the mechanism by which brain organoid transplantation enhances neural regeneration in stroke. Somatic cells can be reprogrammed to produce iPSCs, which can be used for the culture of brain organoids. The 3D aggregation of iPSCs under conditions of neural induction molecules causes the formation of neural rosettes. These structures can be suspended in Matrigel or scaffolds to develop into brain organoids in a spinning bioreactor. Brain organoids are transplanted into injured brains after stroke. Transplanted brain organoids are vascularized by host endothelial cells, and the brain infarct volume is reduced by cell migration and replacement. Moreover, brain organoid transplantation enhances neurogenesis, angiogenesis, synaptic reconstruction, and axonal regeneration after stroke. iPSCs, induced pluripotent stem cells.