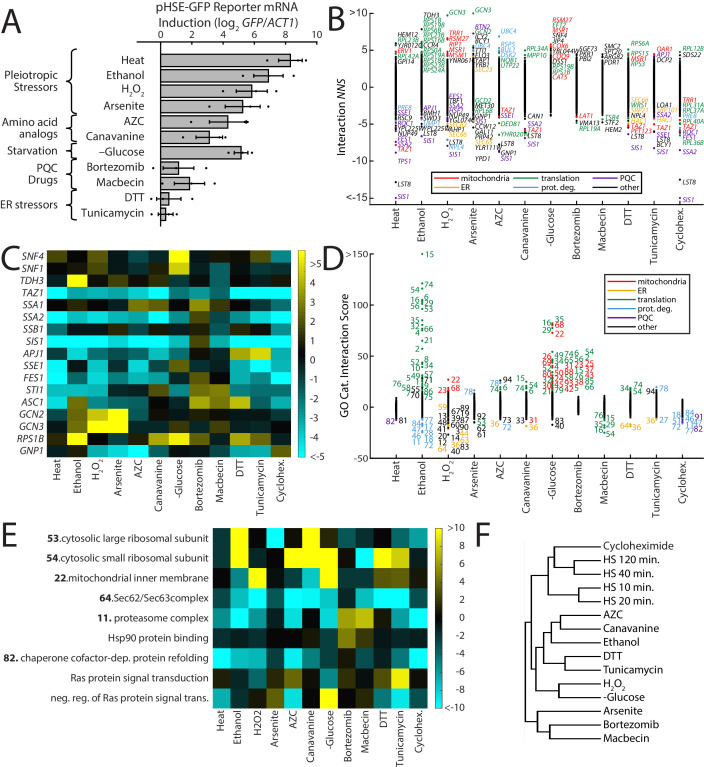
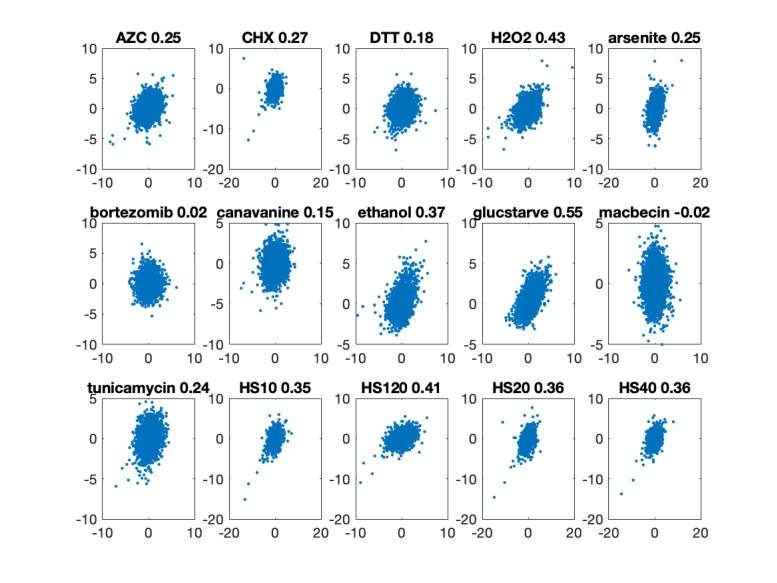
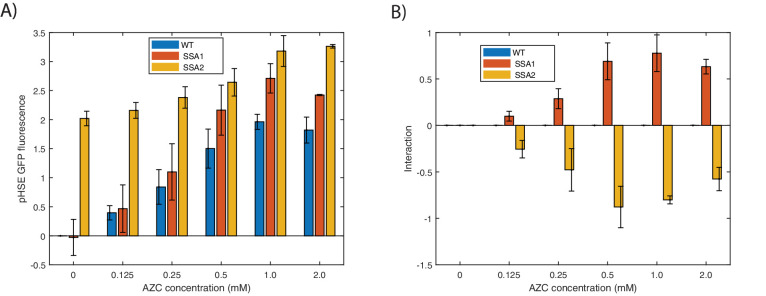
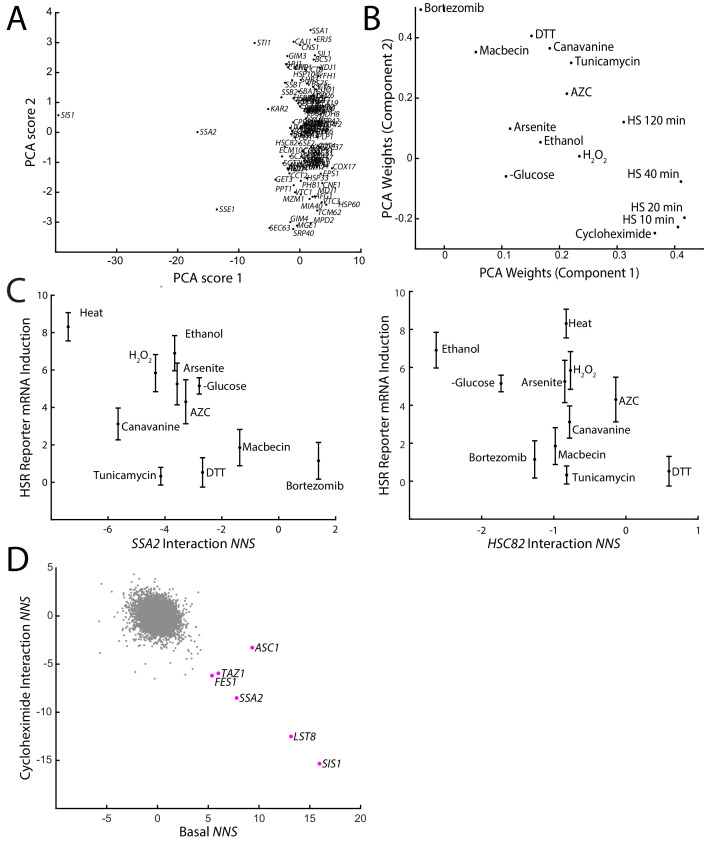
Figure 5. ReporterSeq reveals the diversity of responses to different stress conditions.
(A) HSR reporter mRNA induction based as measured by qPCR in 13 stressors (see Supplementary file 6 for details of treatments). mRNA levels are relative to ACT1 mRNA levels, and the results are normalized such that untreated yeast have an induction of 0. Error bars are standard errors of three replicates. (B) Interaction NNS for each gene under each stressor. Genes with a score magnitude greater than four are labeled (with no more than 12 per condition) and colored based on annotated function. (C) Heat map of interaction NNS for select genes with each stressor. (D) GO category scores for each gene under each stressor. Category ID number key is provided in Supplementary file 7. Outlier categories are colored based on function. (E) Heat map of GO category scores for selected GO categories and each stressor. (F) Hierarchical clustering tree based on gene-stressor interactions. Relatedness between each pair of stressors is quantified by the horizontal length from the branch point.