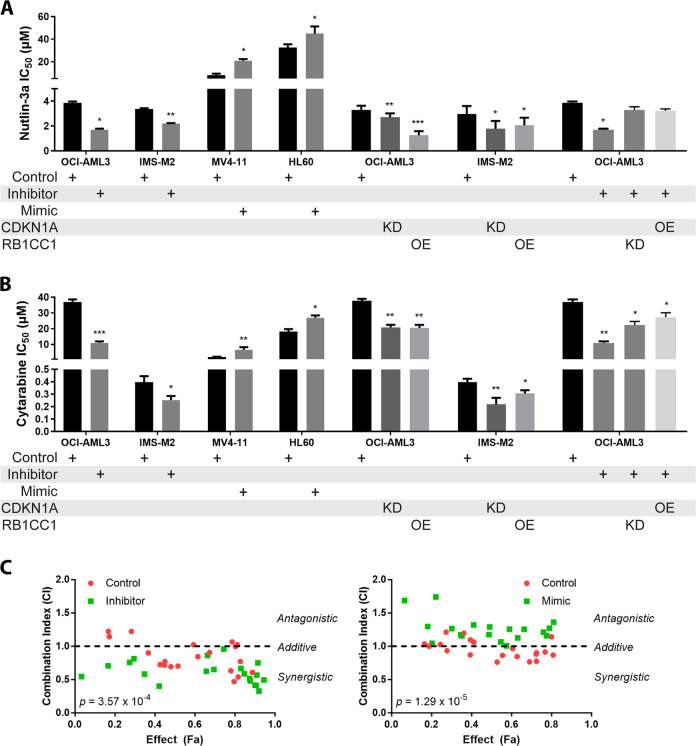
Fig. 5. miR-10a mediates sensitivity to Nutlin-3a and cytarabine in AML.
miR-10a inhibition in the miR-10a-high AML cell lines OCI-AML3 and IMS-M2 resulted in significant sensitization to Nutlin-3a (a) and cytarabine (b). Conversely, overexpression of miR-10a in miR-10a-low AML cell lines MV4–11 and HL60 led to significant resistance. The exogenous overexpression (OE) of Rb1cc1 or knockdown (KD) of p21 alone were sufficient to recapitulate these effects in OCI-AML3 and IMS-M2 cells, confirming that these miR-10a targets are mediators of Nutlin-3a and cytarabine sensitivity. Conversely, the sensitization effects of miR-10a inhibition could be rescued by the knockdown of Rb1cc1 or overexpression of p21. c OCI-AML3 cells transduced with a miR-10a or scrambled control inhibitor (left) and MV4–11 cells transduced with a miR-10a or scrambled control mimic (right) were treated with a combination of Nutlin-3a and cytarabine at various doses and cell viability determined by MTS assay to quantify fractional inhibition of proliferation (Effect (Fa)). The Combination Index (CI) was calculated to determine antagonistic (CI > 1), additive (CI ≈ 1), or synergistic (CI < 1) effects between the two compounds. Nutlin-3a and cytarabine were strongly additive in miR-10a high OCI-AML3 cells but less so in miR-10a-low MV4–11 cells. Drug interactions became synergistic when miR-10a was simultaneously inhibited (p = 3.57 × 10−4), and antagonistic when miR-10a was overexpressed (p = 1.29 × 10−5). (For statistical testing, each treatment was compared to the control within its own group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 by Student’s T test with error bars representing SD (3–6 replicates per experiment)).