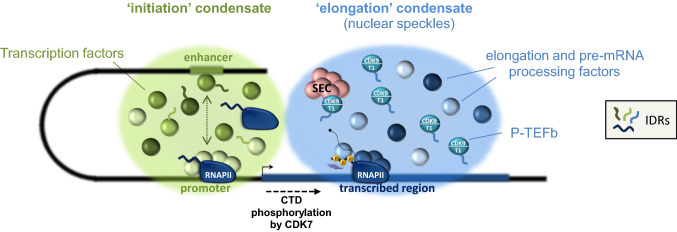
Fig. 4.
Cyclin T1 promotes the formation of ‘elongation condensates’ through liquid–liquid phase separation. Intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) of transcription factors trigger the formation of ‘initiation’ condensates at gene promoters and enhancers and favour recruitment of RNAPII and gene activity. The Cyclin T1 histidine-rich region (HRD) organizes a phase-separated environment that promotes incorporation of P-TEFb into another type of condensate associated with transcription elongation (or nuclear speckles). These condensates simultaneously concentrate pause release, elongation and processing factors. CTD phosphorylation by CDK7 relocates RNAPII from ‘initiation’ to ‘elongation’ condensates, providing RNAPII with critical activities required for the next stage of the transcription cycle. CTD: carboxy-terminal domain