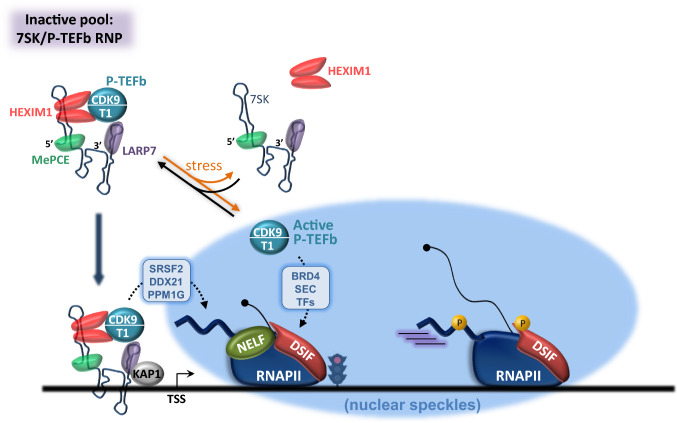
Fig. 5.
Regulation of CDK9 availability by the 7SK snRNP. In the nucleoplasm, a fraction of P-TEFb is sequestered into the 7SK/P-TEFb snRNP, where CDK9 activity is inhibited by HEXIM1 in a 7SK-dependent manner. After cellular stress, disassociation of the 7SK/P-TEFb snRNP releases active P-TEFb, which can be loaded onto target genes by BRD4, Super Elongation Complexes (SEC) or gene-specific transcription factors (TF). The 7SK/P-TEFb snRNP is also directly targeted to gene promoters by KAP1. Factors such as SRSF2, DDX21 or PPM1G can activate P-TEFb from chromatin-anchored 7SK/P-TEFb snRNP in the vicinity of the RNAPII complex for ‘on site’ transcriptional activation. Note that only the active form of P-TEFb can be incorporated into transcription-associated condensates