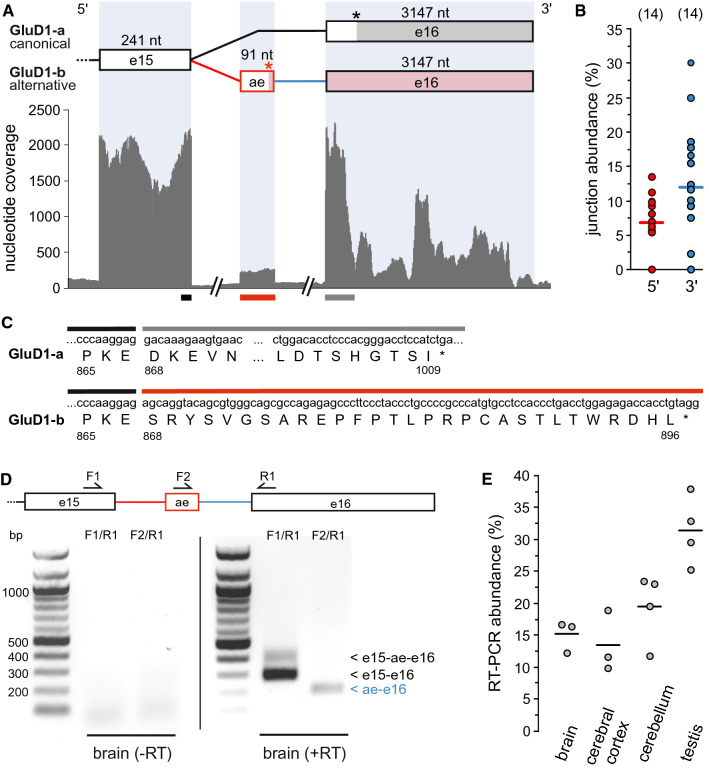
Fig. 3.
De novo identified GluD1-b splicing isoform. A Our analysis revealed the existence of splice junctions, which indicate the incorporation of a 91 nt alternative exon (ae) between canonical exons 15 and 16. The coverage track shows a clearly defined exon (stop codons indicated by asterisks). B 5′- and 3′-junction abundance relative to the canonical junction (median indicated as bars; number of datasets with sufficient coverage given in parenthesis). C Incorporation of the alternative exon results in a hitherto undescribed isoform, GluD1-b, (896 aa), which contains an alternative C-terminus. D RT-PCR detection in human brain RNA. Exon-specific primers (F1/R1) show the amount of transcripts with (376 bp) and without (285 bp) alternative exon. Primers F2/R1 confirm the identity of the alternative exon, which was further confirmed by sequencing. Bands are absent in negative controls without reverse transcriptase (-RT). E Relative amounts of alternative F1/R1 RT-PCR product in RNAs from different human tissues. For further information, see Fig. S18