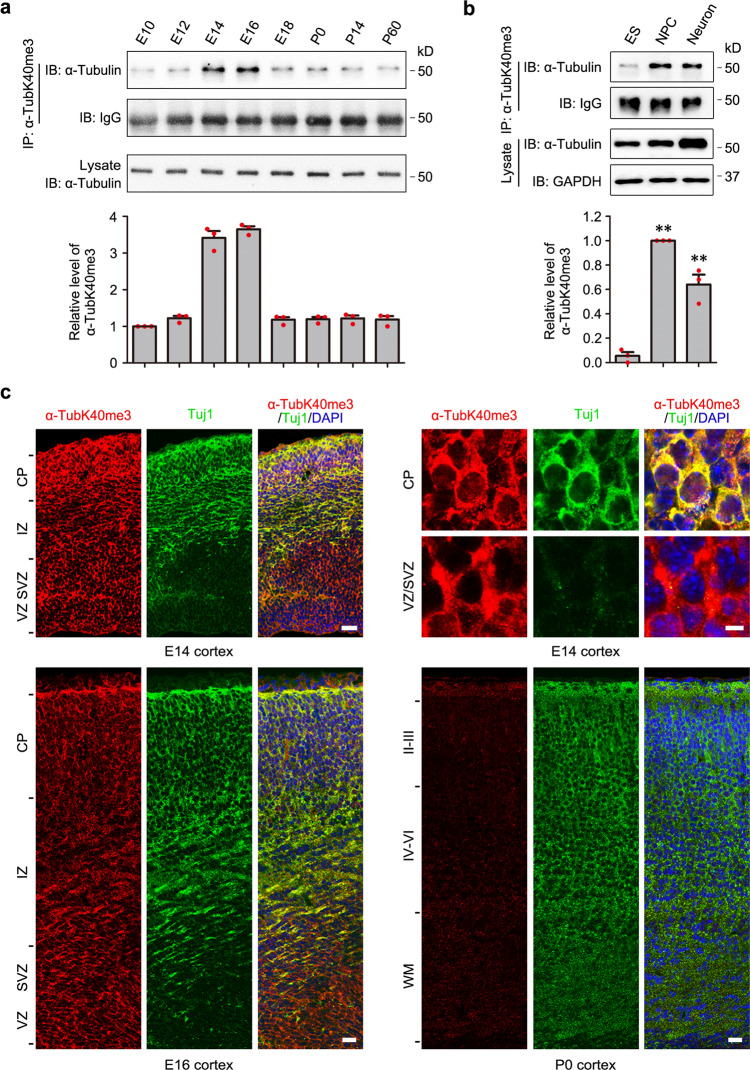
Fig. 1. α-TubK40me3 is temporally regulated during cortical development and occurs in neural progenitor cells and neurons.
a Immunoprecipitation by α-TubK40me3 antibody and following immunoblotting with α-tubulin showed the temporal regulation of α-TubK40me3 at different developing stages of mouse cerebral cortex. α-Tubulin and IgG served as the loading control of whole protein and antibody, respectively. The data were normalized to E10 and shown as the mean ± s.e.m. (n = 3 biological replicates). b Relatively high level of α-TubK40me3 normalized to α-tubulin existed in human NPCs and neurons but not ES cells during neuronal differentiation. GAPDH served as a loading control. The data were normalized to NPCs and shown as the mean ± s.e.m. (n = 3 biological replicates). Data were analyzed using paired two-tailed Student’s t test. **P < 0.01 versus the ES cells. c Immunostaining showed high level of α-TubK40me3 in the CP, IZ, and VZ/SVZ regions of mouse somatosensory cortex at E14 and E16, and large downregulation of α-TubK40me3 at P0. α-TubK40me3 was present in the NPCs of VZ/SVZ and the neurons of CP. Brain slices were stained for α-TubK40me3 (red), Tuj1 (green) and DAPI (blue) (n = 3 biological replicates). Scale bar: 25 μm for the brain slices and 5 μm for the upper-right high magnification. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.