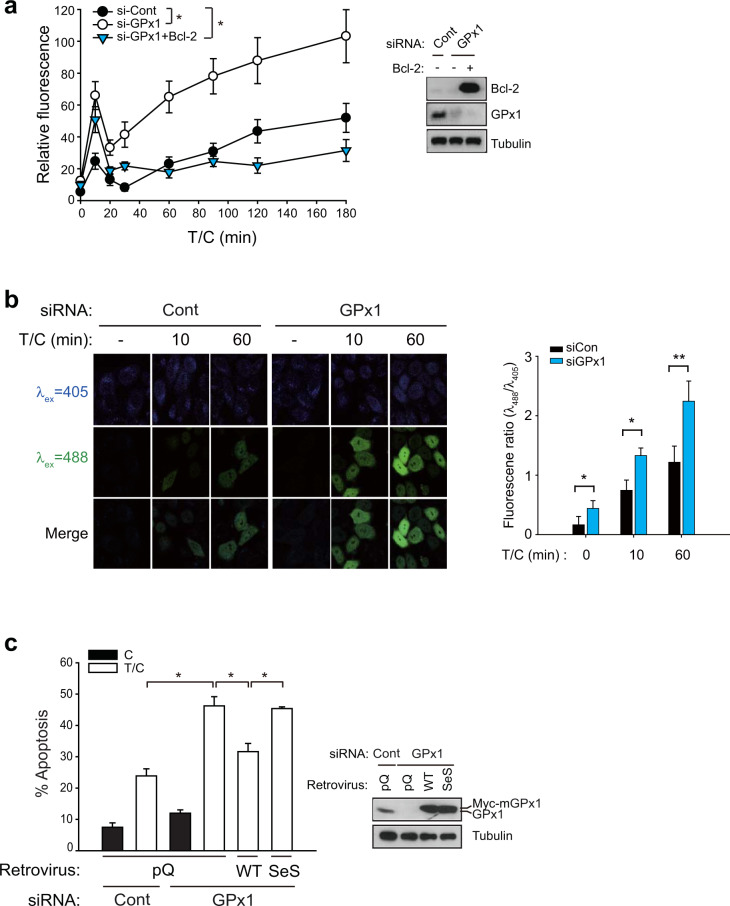
Fig. 2. GPx1 is critical for regulating the intracellular H2O2 level.
a Intracellular ROS levels were determined using 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) treatment of siRNA-transfected HeLa cells following T/C stimulation. Bcl-2-overexpressing HeLa cells were analyzed for comparison. The data in the graph are the means ± SD of relative DCF fluorescence intensities from 80 to 100 cells (n = 3, *P < 0.0001 with repeated-measures ANOVA). b Intracellular H2O2 levels were measured in HyPer-expressing HeLa cells. Fluorescence images were taken of the HyPer-expressing HeLa cells following T/C stimulation. The data in the graph are the means ± SD of the ratio of fluorescence intensities at 488 and 405 nm (n = 15–25 cells). Representative images are shown. c siRNA-transfected HeLa cells were infected with the indicated retroviruses encoding WT mouse GPx1 or an inactive mutant (SeS). The apoptosis rate was measured after T/C stimulation for 6 h. The data in the graph are the means ± SD of the percent of apoptotic cells (n = 3, **P < 0.005). Immunoblots show the level of knockdown and rescued expression of GPx1. Empty retroviral vector (pQ) was used as a control.