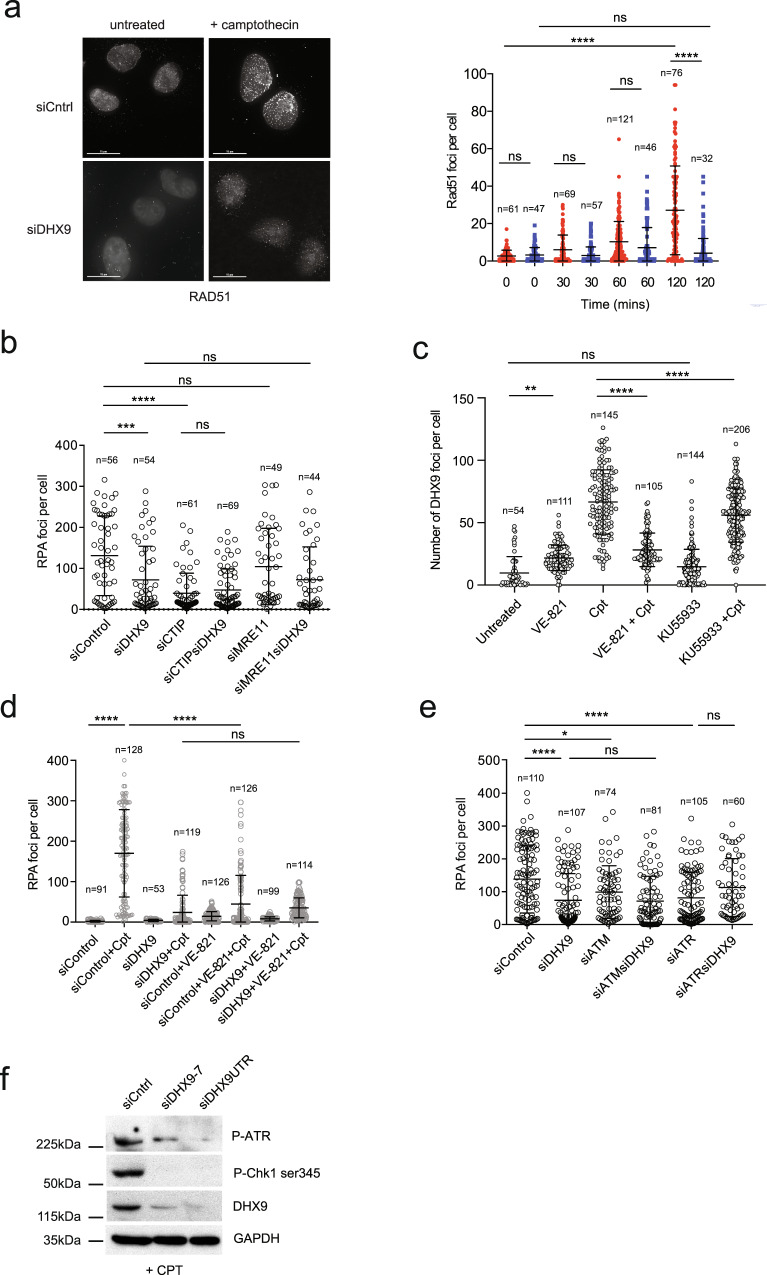
Fig. 5. DHX9 is required for the recruitment of RAD51.
a Fluorescent image (left panel) and quantification (right panel) showing the decreased formation of RAD51 foci in control U2OS cells (red) and cells knocked down for DHX9 (blue) treated with 1 μM camptothecin for 2 h then left for 2 h to recover. b DHX9 is in a common genetic pathway for the formation of RPA foci with CTIP and MRE11. RPA foci in cells knocked down using siRNA for the indicated genes are shown. Cells were treated with 1 μM camptothecin for 2 h. c Recruitment of DHX9 to foci is dependent on ATM and ATR. Wild-type cells were inhibited for ATR and ATM using VE-821 and KU55933, respectively. d, e DHX9 is in a common genetic pathway for the formation of RPA foci with ATR and ATM. RPA foci are shown for cells treated with inhibitors for ATR (VE-821) and ATM (KU55933) (d) or knocked down with siRNA against ATM and ATR (e). f Western blot showing that knockdown of DHX9 impairs Cpt induced autophosphorylation of ATR on Thr1989 and phosphorylation of Chk1 on ser 345. Quantification of n cells (as indicated) from three pooled biologically independent experiments were performed in (a–e). Means of data sets were shown to be significantly different using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. (ns not significant, *p < 0.1, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001). Error bars indicating one standard deviation are also indicated. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.