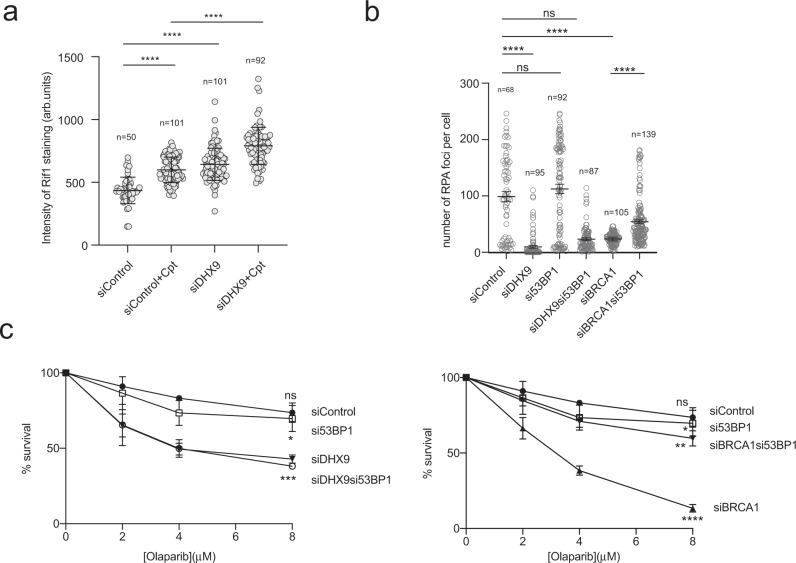
Fig. 8. Defects in DHX9 are not suppressed by knockdown of 53BP1.
a DHX9 suppresses the recruitment of RIF1 to chromatin in response to camptothecin-induced DNA damage. The intensity of chromatin-bound RIF1 staining is plotted. Mean and standard deviation are indicated. b Defect in the recruitment of RPA into foci in DHX9 defective cells is only partially restored by knockdown of 53BP1. A number of RPA foci is plotted for cells knocked down for the indicated genes using siRNA. Quantification of n cells (as indicated) from three pooled biologically independent experiments were performed in (a) and (b). c Knockdown of 53BP1 does not restore Olaparib resistance to DHX9 depleted cells in a clonogenic survival assay (left panel) but does restore Olaparib resistance to BRCA1 defective cells (right panel). The data sets for DHX9 and BRCA1 were performed concurrently, with the same controls, but are depicted separately for presentation purposes. Survival values were quantified from n = 3 biologically independent experiments. (a–c) Statistical analysis performed using one-way ANOVA and multiple comparisons analysed using post hoc Tukey’s test in (a) and (b). (ns not significant, *p < 0.1, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001). Means and error bars indicating one standard deviation are also indicated. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.