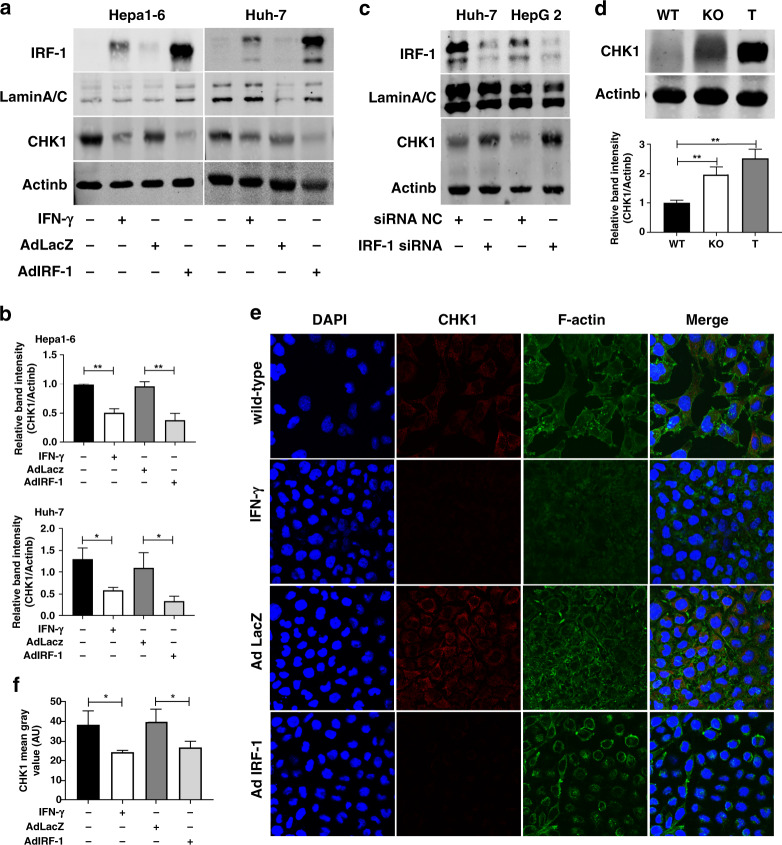
Fig. 2. IFN-γ represses CHK1 through IRF-1 in HCC cells.
a Nuclear IRF-1 protein and whole cell lysate for CHK1 protein expression are measured by western blot in Hepa1-6 cells and Huh-7 cells induced by mouse IFN-γ (50 u/ml)/human IFN-γ (100 u/ml) for 24 h, or infected by mouse/human AdIRF-1 (50 MOI) for 48 h, respectively. b Quantification of CHK1 protein expression in Hepa1-6 cells (upper) and Huh-7 cells (lower) are from three independent experiments. Data represent mean ± SD. c IRF-1 protein (40 µg) and CHK1 protein expression are detected by western blot in Huh-7 cells and HepG2 cells transfected with human IRF-1 siRNA or negative control (NC) for 48 h. d Basal CHK1 protein expression (upper) is determined by western blot in liver from IRF-1−/− (KO) or wild-type (WT) B6 mouse, and in Hepa1-6 tumour from WT B6 mouse (T). Quantification of CHK1 protein expression (lower) is from three mice, respectively. e Immunofluorescent images (×400 magnification) of CHK1 (red staining) are shown for Hepa1-6 cells induced by mouse IFN-γ (50 u/ml) for 24 h or infected by mouse AdIRF-1 (50 MOI) for 48 h. f Quantification of CHK1 (AU) from three independent experiments are shown for Hepa1-6 cells induced by IFN-γ or infected by either AdLacZ or AdIRF-1. Data represent mean ± SD. Western blot and immunofluorescent results shown are representative image from three independent experiments.