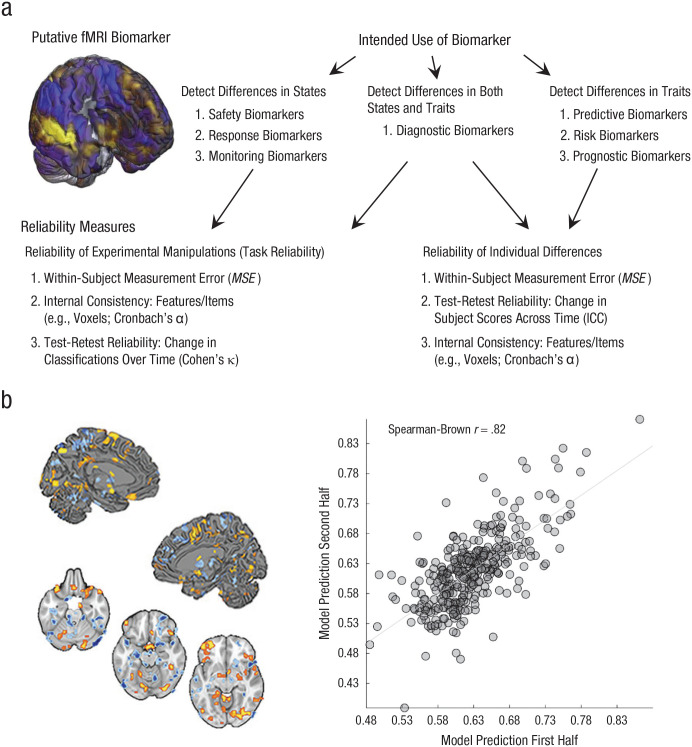
Fig. 1.
Use cases for functional MRI (fMRI) biomarkers and an example of test-retest reliability. Among the seven major categories of biomarkers defined by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (a), some (i.e., predictive, risk, and prognostic biomarkers) are designed to measure variation between individuals (e.g., to measure traitlike variables such as risk for depression, trait anxiety, or vulnerability to drug overdose). These biomarkers depend on measuring stable interindividual differences and thus require long-term test-retest reliability, which is typically estimated by calculating the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) for continuous variables or Cohen’s κ for binary variables. Other biomarkers (i.e., safety, pharmacodynamic, monitoring, and response biomarkers) rely on the ability to measure variation within an individual across time, mental or physiological states, or treatment doses. Detecting within-person states relies less on stable individual differences than stable mappings between measure and state (in fMRI, between the brain and mental states and outcomes) with large and consistent effect sizes, referred to as task reliability (Hedge et al., 2018). This depends on low within-person measurement error (e.g., MSE) and can be measured with ICC or κ. For biomarkers related to dynamic states, other characteristics that increase test-retest reliability, including between-person heterogeneity and long-term stability across time, can be irrelevant or even undesirable. Reliability (b) is shown for a multivariate signature of risk for cardiovascular disease (figure adapted from Gianaros et al., 2020). The brain images depict significant pattern weights fitted on brain responses to affective images that positively (warm colors) and negatively (cool colors) contribute to the prediction of a marker of preclinical atherosclerosis. The scatterplot (with best-fitting regression line) depicts data used to estimate split-half reliability (N = 338).