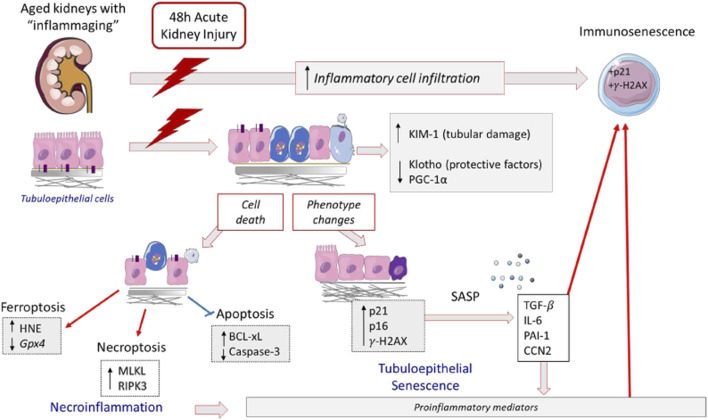
FIGURE 10.
Proposed mechanisms involved in aging-related FA-AKI increased susceptibility. In response to FA injury, aging kidneys present an increase of KIM-1 expression, indicator of tubular damage, lower levels of nephroprotective factors and immunosenescent infiltrating cells. The tubular cell damage can be lethal; in FA-aging kidneys there is an activation of inflammatory forms of cell death, such as necroptosis and ferroptosis, as well as an inhibition of apoptosis. In aging kidneys, injured tubular cells change their phenotype to a proinflammatory and senescent one, being IL-6 one of the most upregulated cytokines. These cellular and molecular changes may partially underlie the age-related increased susceptibility to developing more severe AKI in response to FA.