Figure 8 .
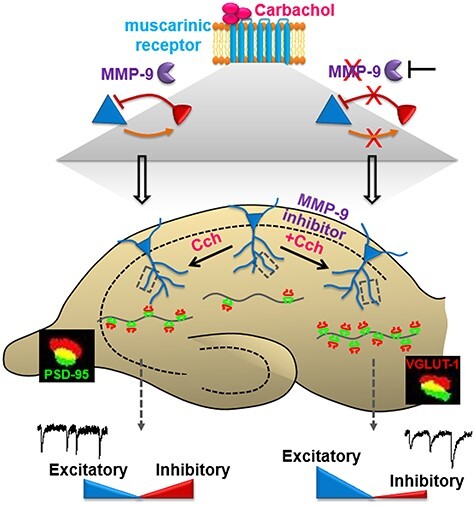
Graphical summary: cholinergically induced MMP-9 activity mediates the modulation of the excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission. Activation of cholinergic muscarinic receptors triggers an enhancement of inhibitory currents input onto hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons (blue), and in turn, a potentiation of fast-spiking inhibitory neurons (red) via the increase of excitatory currents input. Both synaptic connections from inhibitory to excitatory neurons and vice versa are facilitated by the activity of MMP-9. Blocking the MMP-9 activity leads to an even larger boost of excitatory currents input onto the CA1 pyramidal neurons, while preventing the inhibitory currents potentiation. These unbalanced excitatory and inhibitory transmissions strongly potentiate the growth of synaptic connections in the CA1 pyramidal neurons, while only a moderate increase in synapse number is induced by cholinergic activation when MMP-9 is active.
