Figure 8.
Mechanism of the E-field control of magnetic switching
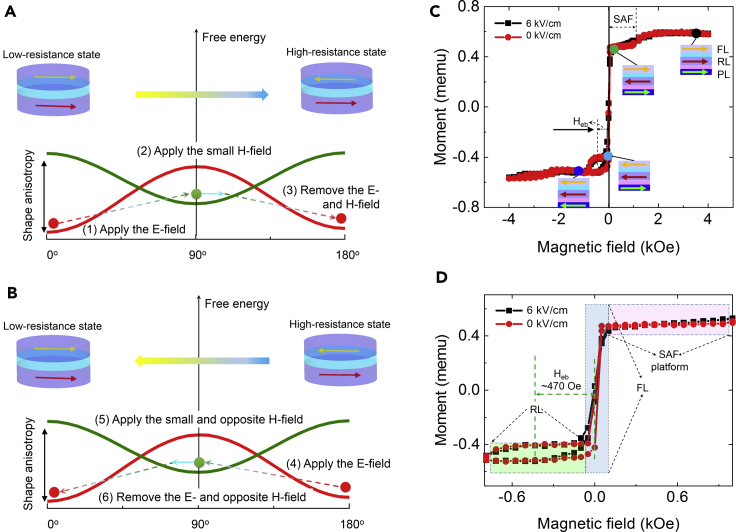
(A) Schematic of 180° magnetization switching from a low-resistance to high-resistance state from the perspective of the FL free energy. (B) Schematic of 180° magnetization switching back from a high-resistance to low-resistance state from the perspective of the FL free energy. The competition among the E-field-induced magnetoelastic anisotropy energy, the magnetic shape anisotropy energy, and the Zeeman energy is the driving force for the E-field-controlled magnetic switching.
(C) Magnetic hysteresis for the unpatterned MTJs under in-situ E-fields along the major-axis direction.
(D) Magnified moment vs. magnetic field (M-H) hysteresis around the low H-field switching region for the FL and RL with the assistance of the E-fields.