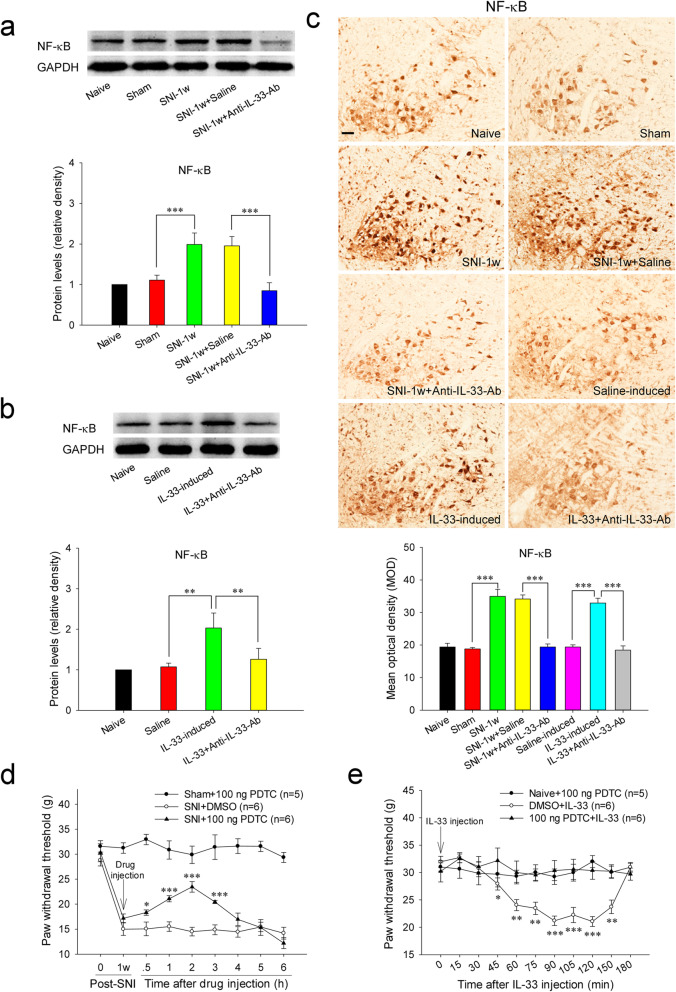
Fig. 3.
Red nucleus IL-33 facilitates the early development of mononeuropathic pain by activating NF-κB signaling pathway. A Western blotting showed an upregulated NF-κB in the RN at 1 week post-SNI, intrarubral administration of anti-IL-33 antibody restrained the overexpression of NF-κB (n = 6 per group, F = 12.766, P < 0.001). B Western blotting showed that intrarubral injection of IL-33 stimulated the protein expression of NF-κB in naive rats (n = 6 per group, F = 7.497, P = 0.003). C Immunohistochemistry demonstrated that NF-κB was increased in the RN of SNI rats (F = 41.250, P < 0.001) and IL-33-induced hypersensitivity rats (F = 34.509, P < 0.001) (n = 4 per group). D Intrarubral injection of NF-κB inhibitor PDTC at 1 week post-injury attenuated SNI-induced mononeuropathic pain compared to DMSO control (n = 5–6 per group, F = 135.298, P < 0.001). E PDTC pre-injected into the RN, 30 min ahead of IL-33 administration, relieved IL-33-evoked mechanical hypersensitivity compared to DMSO control (n = 5-6 per group, F = 97.341, P < 0.001). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. Scale bars = 50 μm