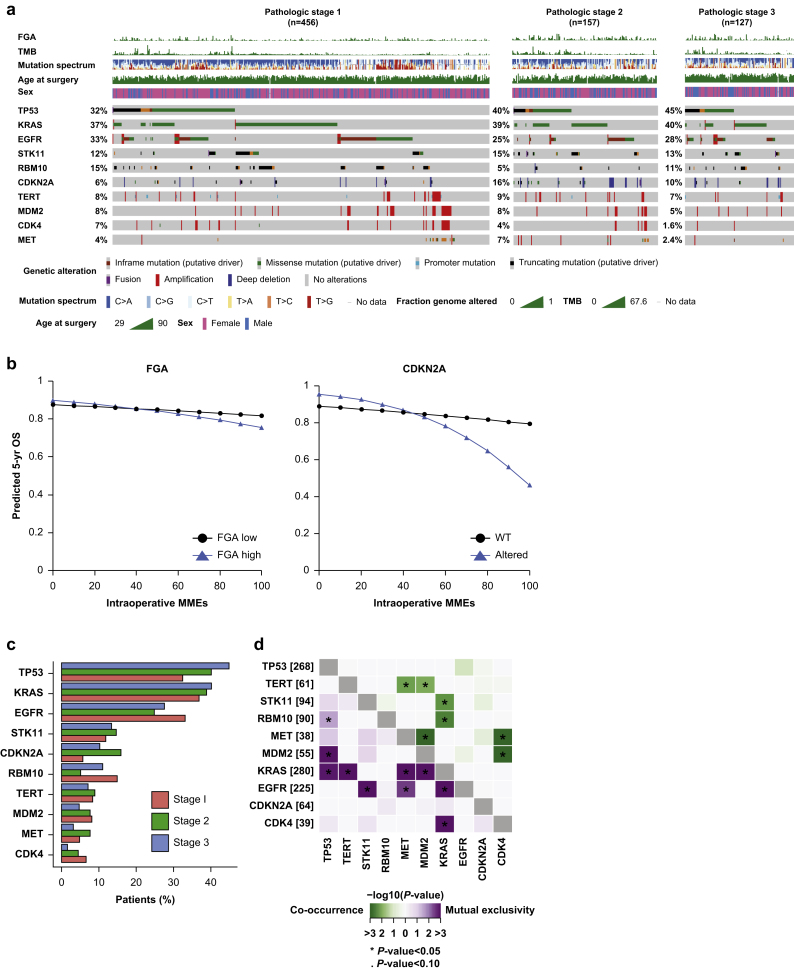
Fig 3.
Association between intraoperative opioid dose and genomic alterations in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. (a) OncoPrint of alteration frequencies of all genes altered ≥5% for the overall study cohort. Patients are subdivided by pathologic tumour stage. (b) Five-year predicted overall survival (OS) for patients with high and low fraction genome altered and altered and wild-type (WT) CDKN2A with increasing intraoperative morphine milligram equivalents (MMEs). (c) Comparative bar graphs representing the alteration rate for each genomic factor by stage. (d) Co-occurrence and mutual exclusivity between genes across all tumours. FGA, fraction genome altered; TMB, tumour mutational burden.